The seventh class of my 12-week Creating Science Fiction course at George Brown College is all about short story writing. I’m by nature a progressive—and an itinerant explorer; so, I am updating materials for my students and sharing them with you.
 One resource I’m eager to introduce to my students is Canadian SF short story writer Douglas Smith’s recent guidebook, Playing the Short Game: How to Market & Sell Short Fiction. Smith’s guidebook is a Tardis-style smallish yet comprehensive guide on what it takes to be a successful short story writer from starting & finishing to marketing & publishing to leveraging & promotion.
One resource I’m eager to introduce to my students is Canadian SF short story writer Douglas Smith’s recent guidebook, Playing the Short Game: How to Market & Sell Short Fiction. Smith’s guidebook is a Tardis-style smallish yet comprehensive guide on what it takes to be a successful short story writer from starting & finishing to marketing & publishing to leveraging & promotion.
Smith is an accomplished short story writer and marketer, who has always openly shared his treasures of acquired wisdom with others. His stories have appeared in thirty countries and 25 languages. He’s won three awards and has three acclaimed collections—so far. For years, his Foreign Market List has helped writers—including me—sell their work all over the world. To date, I have sold short stories (mostly translated reprints) to markets in Greece, Poland, Romania, Israel, and Italy—thanks to his list.
Why Write Short?
 I’m a petite five foot-three height and purposely wear flat shoes. I love short. I prefer my espresso pulled in short shots—or ristretto—in my flat white. Described as bolder, fuller, with more body and less bitterness, the ristretto is like a burst of intense flavor with a lingering finish. Short is pretty cool.
I’m a petite five foot-three height and purposely wear flat shoes. I love short. I prefer my espresso pulled in short shots—or ristretto—in my flat white. Described as bolder, fuller, with more body and less bitterness, the ristretto is like a burst of intense flavor with a lingering finish. Short is pretty cool.
Douglas Smith gives seven excellent reasons for writing short fiction, even if you are ultimately a novel writer, like me. Writing short stories:
- Helps you learn your craft in easy, short-term, bite-sized amounts and over a reasonable time for you to learn, apply, and relearn
- Helps you test the waters of literature, to discover what excites you, provokes you and what ultimately you NEED to express
- Builds your resume, again more easily and quickly than a novel, toward that ultimate novel; publishers of magazines and publishing houses are more likely to take your work seriously if you have a publishing history
- Helps you explore ideas for your novel, by “pinging” certain premises you may wish to explore in further detail or take elsewhere in a novel
- Helps you build a backlist of published stories, which you own, once rights have reverted back to you
- Helps you build a network in your writing community of publishing houses, editors, other writers and so forth as you submit and exchange through your works and letters (including all those rejections!). Eventually, a pleased editor/publisher may invite you to submit to a “Best of” anthology or provide a collection. This has happened to me several times.
- Helps you learn the publishing business (well, sort of, says Smith…). Through exposure to the business side of publishing, you will gain an appreciation of how the publishing world works.
Know What You’re Writing
 A short story only has 7,000 or less words to get your tale across while a novel has over ten times that many words to do the same. It follows then that the short story format is a simpler one. This does not necessarily mean easier.
A short story only has 7,000 or less words to get your tale across while a novel has over ten times that many words to do the same. It follows then that the short story format is a simpler one. This does not necessarily mean easier.
Novels provide a sense of change, growth and solutions to problems and conflicts. “The short story doesn’t have the luxury of depicting change; the closest it can come is awareness,” writes Shelley Lowenkopf in her 2007 article “Telling Tales” in The Portable Writer’s Conference: Your Guide to Getting Published by Quill Driver Books.
She goes on to describe the short story as a close-up to a novel’s landscape. The short story is, therefore, often more intense and powerful. A short story, more than a novel, has the power to transport, disturb and enlighten.
 Renowned short story authors like Edgar Allen Poe, Nathanial Hawthorne, and Somerset Maugham, emphasize the importance of striving for one effect when writing a short story: the single effect you wish to leave with the reader at the end. This is accomplished by selecting events or situations that build quickly into a combustible response. Even Alice Munro, who is known for cramming long timeframes into her short stories, frames time through a single event: a meal, family gathering, wedding or funeral, for instance.
Renowned short story authors like Edgar Allen Poe, Nathanial Hawthorne, and Somerset Maugham, emphasize the importance of striving for one effect when writing a short story: the single effect you wish to leave with the reader at the end. This is accomplished by selecting events or situations that build quickly into a combustible response. Even Alice Munro, who is known for cramming long timeframes into her short stories, frames time through a single event: a meal, family gathering, wedding or funeral, for instance.
Jack Bickham, in his book, Elements of Fiction Writing: Scene and Structure by Writer’s Digest Books (1993) writes that, “story length, author intention, traditional expectations of the audience, and all sorts of things may affect the form a story may take.” Choosing the appropriate length to tell your story relies on the complexity of your premise and theme.
Understanding the Short Story Format
Here are seven tips toward writing a compelling and memorable short story:
- Open in the middle of something happening (e.g., action/in a “scene”)
- Make your opening provocative (raise the stakes as high as you can)
- Write scenes and write sparingly (avoid describing the obvious—use description to show something odd, memorable, exotic)
- Have characters define themselves and their goals through what they do and observe (e.g., show more than tell)
- Define characters with dialogue (a great way to reveal while keeping a high pace)
- Withhold vital information for as long as possible
- Don’t explain the ending (cut down on the denouement; let the reader make those conclusions—a key in the short story format)
Selling Your Short Story
Smith’s guidebook provides several chapters of excellent advice in logical steps toward a successful career.
Here are just a few gems that I will be sharing with my students.
First of all, remember that you are not selling your story; you’re licensing a particular set of rights for someone to do something with that story. Before you do anything else, do your homework: know the rights you’re selling; and which ones to keep. Smith describes five major types of rights: media; language; geography (less and less relevant); occurrence; and time.

Eramosa River, Ontario (photo by Nina Munteanu)
Media rights include print rights, electronic rights and audio rights. Markets include magazines, anthologies and collections for short stories. Language and geography rights are pretty self-explanatory. Occurrence rights relate to whether the publisher is buying first or second and onward rights (otherwise known as reprints). Most publishers prefer to pay for the right to publish your work for the first time in that particular format (e.g., in print and in English, for instance). Having said that, I’ve had a lucrative history of selling reprints to some of my more popular short stories. I’ve furthered gone on to selling other rights, such as foreign language rights and audiobook and e-book rights. I’ve also sold two short story collections, one to an Italian publisher (coming out this year) and shorts in several anthologies. No movies yet… But I did have a serious discussion with a writer/producer on one of my shorts. Recall how many Philip K. Dick short stories have been adapted to movies (e.g., Total Recall, The Adjustment Bureau, Paycheck, Minority Report, and Blade Runner).
Heinlein’s Five Rules of Writing
Smith evokes SF writer Robert J Heinlein’s 5 rules of writing to succeed as a short story writer (as any kind of writer, actually). These are:
- You must write
- You must finish what you write
- You must refrain from rewriting, except to editorial order
- You must put the work on the market
- You must keep the work on the market until sold
I know… Number 3 sounds pretty suspicious, or arrogant at the very least. As Robert J. Sawyer concludes on his site in reference to the five rules, number 3 is open to reasonable interpretation. Of course, it must mean AFTER you’ve finished and edited the story with some level of confidence that you’re happy with it—never mind what other people think of it.
 Nina’s Bus-Terminal Model
Nina’s Bus-Terminal Model
In my writing guide The Fiction Writer, Chapter L (for “Long or Short?”), I talk about how I launched my own successful short story writing career. I’d been writing short stories for a few years without much success (I was getting interesting rejection letters, so I knew I was getting close); then I settled into a kind of model/routine. I call it The Bus Terminal Approach. As Smith attests—several times—it’s a numbers game. That’s how I played it. It starts with one story and relies on you not waiting until you write the next, and the next and the next. Here’s how it works:
- You list at least 3 markets that you’ve researched for Story A and send it to the first of the three
- You start right away writing Story B, send it to the first of 3 markets you’ve researched and listed for it
- When Story A rejection arrives, you do not revise but send it right away to the second market
- Same thing for Story B
- Write Story C and treat similarly
 Remember to keep track of what you send where and when and what happens to it. It can become a very confusing bus terminal otherwise, with someone ending up in Seattle when they are headed to Toronto! What happens with this approach is several things: you begin to treat the whole marketing/publishing process as a business (which it is) and because you have so many “buses” out there coming and going, the rejections don’t hurt quite as much and instead become part of the learning process, which they should be. You adopt a more business-like approach, which translates into your relationship with editors and publishers. A win-win situation results. Believe me; this works. Once I fell into this method, my sales increased by over 70%.
Remember to keep track of what you send where and when and what happens to it. It can become a very confusing bus terminal otherwise, with someone ending up in Seattle when they are headed to Toronto! What happens with this approach is several things: you begin to treat the whole marketing/publishing process as a business (which it is) and because you have so many “buses” out there coming and going, the rejections don’t hurt quite as much and instead become part of the learning process, which they should be. You adopt a more business-like approach, which translates into your relationship with editors and publishers. A win-win situation results. Believe me; this works. Once I fell into this method, my sales increased by over 70%.
Several of my stories are currently available in a collection entitled Natural Selection by Pixl Press. You can read one of my short stories right on Amazing Stories: “Virtually Yours”.
My guidebook, The Fiction Writer, can be purchased in various online and onsite bookstores, including Amazon, Kobo, Chapters Online, Barnes & Noble, and several others even I don’t know about.
 Nina Munteanu is an ecologist and internationally published author of award-nominated speculative novels, short stories and non-fiction. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s recent short story is the bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” (Mincione Edizioni, Rome). Her latest “Water Is…” is currently an Amazon Bestseller and NY Times ‘year in reading’ choice of Margaret Atwood.
Nina Munteanu is an ecologist and internationally published author of award-nominated speculative novels, short stories and non-fiction. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s recent short story is the bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” (Mincione Edizioni, Rome). Her latest “Water Is…” is currently an Amazon Bestseller and NY Times ‘year in reading’ choice of Margaret Atwood.

 “I write SF about a near future ‘Gaian’ world too, and at times felt I was reading a prequel to my own novels, but that’s not why I rated this collection so highly. I did so for two reasons. First, because the science was so interesting, combining visionary metaphysical speculation with AI corporate tech in scenarios that often seemed chillingly possible. Second, because of the author’s focus on the effects of these developments on human beings with complex pasts and desires. Jealousy, lust, loneliness, grief and love are all drivers of these taut and fascinating narratives…”–Amazon Review
“I write SF about a near future ‘Gaian’ world too, and at times felt I was reading a prequel to my own novels, but that’s not why I rated this collection so highly. I did so for two reasons. First, because the science was so interesting, combining visionary metaphysical speculation with AI corporate tech in scenarios that often seemed chillingly possible. Second, because of the author’s focus on the effects of these developments on human beings with complex pasts and desires. Jealousy, lust, loneliness, grief and love are all drivers of these taut and fascinating narratives…”–Amazon Review Evolution is the language of destiny. What is destiny, after all, but self-actualization and synchronicity? If evolution is the language of destiny, then choice and selection are the words of evolution and “fractal ecology” is its plot.
Evolution is the language of destiny. What is destiny, after all, but self-actualization and synchronicity? If evolution is the language of destiny, then choice and selection are the words of evolution and “fractal ecology” is its plot. On the vertical argument, the French naturalist Jean-Baptiste Lamark developed a theory of biological evolution in the early 19th century considered so ridiculous that it spawned a name: Lamarkism. His notion—that acquired traits could be passed along to offspring—was ridiculed for over two hundred years. Until he was proven right. Evolutionary biologists at Tel Aviv University in Israel showed that all sorts of cellular machinery—an intelligence of sorts—played a vital role in how DNA sequences were inherited. When researchers inserted foreign genes into the DNA of lab animals and plants, something strange happened. The genes worked at first; then they were “silenced”. Generation after generation. The host cells had tagged the foreign genes with an “off switch” that made the gene inoperable. And although the new gene was passed onto offspring, so was the off switch. It was Larmarkism in action: the parent’s experience had influenced its offspring’s inheritance. Evolutionists gave it a new name. They called it soft inheritance.
On the vertical argument, the French naturalist Jean-Baptiste Lamark developed a theory of biological evolution in the early 19th century considered so ridiculous that it spawned a name: Lamarkism. His notion—that acquired traits could be passed along to offspring—was ridiculed for over two hundred years. Until he was proven right. Evolutionary biologists at Tel Aviv University in Israel showed that all sorts of cellular machinery—an intelligence of sorts—played a vital role in how DNA sequences were inherited. When researchers inserted foreign genes into the DNA of lab animals and plants, something strange happened. The genes worked at first; then they were “silenced”. Generation after generation. The host cells had tagged the foreign genes with an “off switch” that made the gene inoperable. And although the new gene was passed onto offspring, so was the off switch. It was Larmarkism in action: the parent’s experience had influenced its offspring’s inheritance. Evolutionists gave it a new name. They called it soft inheritance.



 She imagines its coolness gliding down her throat. Wet with a lingering aftertaste of fish and mud. She imagines its deep voice resonating through her in primal notes; echoes from when the dinosaurs quenched their throats in the Triassic swamps.
She imagines its coolness gliding down her throat. Wet with a lingering aftertaste of fish and mud. She imagines its deep voice resonating through her in primal notes; echoes from when the dinosaurs quenched their throats in the Triassic swamps. Emilie Moorhouse of
Emilie Moorhouse of  “…In an interesting scarcity future in which we follow the fate of a character abandoned by her mother, water itself becomes a character. In the second paragraph we’re told that “Water is a shape shifter,” and in the next page we encounter the following description: “Water was paradox. Aggressive yet yielding. Life-giving yet dangerous. Floods. Droughts. Mudslides. Tsunamis. Water cut recursive patterns of creative destruction through the landscape, an ouroboros remembering.” These descriptive musings cleverly turn out to be more than metaphors and tie in directly to the tale’s surprising ending.”—Alvaro Zinos-Amaro,
“…In an interesting scarcity future in which we follow the fate of a character abandoned by her mother, water itself becomes a character. In the second paragraph we’re told that “Water is a shape shifter,” and in the next page we encounter the following description: “Water was paradox. Aggressive yet yielding. Life-giving yet dangerous. Floods. Droughts. Mudslides. Tsunamis. Water cut recursive patterns of creative destruction through the landscape, an ouroboros remembering.” These descriptive musings cleverly turn out to be more than metaphors and tie in directly to the tale’s surprising ending.”—Alvaro Zinos-Amaro,  Water Is… The Meaning of Water
Water Is… The Meaning of Water





 But Joshua is a spirited creek – in spite of all it has been through, Joshua Creek is among the top two urban creeks for healthy water quality, and is still inhabited by a variety of aquatic animals like small fish and insects. Joshua Creek is home to forests, wetlands and thickets with around 150 plant species, and provides an important natural habitat corridor for the movement of birds and other animals, including migratory species. Rather than exclusively shrinking, there are also areas of Joshua Creek that are actually in the middle of regrowing their forests, and in spite of everything, Joshua still retains some beautiful gems of natural areas.”
But Joshua is a spirited creek – in spite of all it has been through, Joshua Creek is among the top two urban creeks for healthy water quality, and is still inhabited by a variety of aquatic animals like small fish and insects. Joshua Creek is home to forests, wetlands and thickets with around 150 plant species, and provides an important natural habitat corridor for the movement of birds and other animals, including migratory species. Rather than exclusively shrinking, there are also areas of Joshua Creek that are actually in the middle of regrowing their forests, and in spite of everything, Joshua still retains some beautiful gems of natural areas.”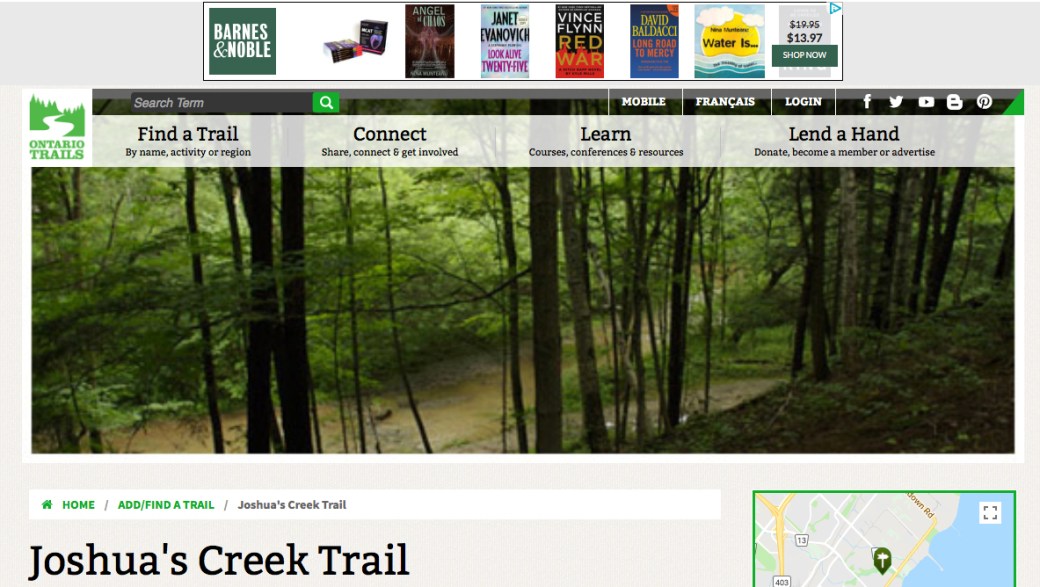
 Nina Munteanu’s “The Way of Water” and the anthology in which it appears was recently praised by Emilie Moorhouse in Prism International Magazine, in a review entitled
Nina Munteanu’s “The Way of Water” and the anthology in which it appears was recently praised by Emilie Moorhouse in Prism International Magazine, in a review entitled  “The Way of Water” (La natura dell’acqua) was translated by Fiorella Smoscatello for Mincione Edizioni. Simone Casavecchia of SoloLibri.net, describes “The Way of Water” in her review of the Italian version:
“The Way of Water” (La natura dell’acqua) was translated by Fiorella Smoscatello for Mincione Edizioni. Simone Casavecchia of SoloLibri.net, describes “The Way of Water” in her review of the Italian version:
 “The Way of Water” will also appear alongside a collection of international works (including authors from Greece, Nigeria, China, India, Russia, Mexico, USA, UK, Italy, Canada (yours truly), Cuba, and Zimbabwe) in Bill Campbell and Francesco Verso’s
“The Way of Water” will also appear alongside a collection of international works (including authors from Greece, Nigeria, China, India, Russia, Mexico, USA, UK, Italy, Canada (yours truly), Cuba, and Zimbabwe) in Bill Campbell and Francesco Verso’s  Nina Munteanu is an ecologist, limnologist and internationally published author of award-nominated speculative novels, short stories and non-fiction. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit
Nina Munteanu is an ecologist, limnologist and internationally published author of award-nominated speculative novels, short stories and non-fiction. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit  Nina Munteanu’s near-future speculative short story “The Way of Water” in Bruce Meyer’s (editor) “Cli Fi: Canadian Tales of Climate Change”, published by
Nina Munteanu’s near-future speculative short story “The Way of Water” in Bruce Meyer’s (editor) “Cli Fi: Canadian Tales of Climate Change”, published by  A bilingual print book by
A bilingual print book by  ” ‘The Way of Water’ is to be ‘a shapeshifter,’ says Nina Munteanu in her dystopian narrative, where she draws a dark scenario and, unfortunately, not too improbable in the near future. In the universe of the story water has become a very precious commodity: rationed consumption, credits (always of water) accounted for and debts collected…The Chinese multinationals have exchanged the public debt of other states with their water reserves with which, now, they can control the climate, deciding when and where it will rain. Who understands this dirty game has been silenced, like Hilda’s mother, a limnologist, inexplicably arrested and never returned; like the daughter of two water vendors, mysteriously disappeared, after having decided not to bow to economic powers: Hanna, who now prefers secure virtual identities to evanescent real appearances. Water. The two, like the covalent bond of a complex molecule, develop a relationship of attraction and repulsion that will first make them meet and then, little by little, will change into a tormented love but, at the same time, so pure as to cause Hilda at great risk, to make an extreme decision that will allow Hanna to realize the strange prophecy that the internal voice, perhaps the consciousness of water, had resonated in the two women for a long time.
” ‘The Way of Water’ is to be ‘a shapeshifter,’ says Nina Munteanu in her dystopian narrative, where she draws a dark scenario and, unfortunately, not too improbable in the near future. In the universe of the story water has become a very precious commodity: rationed consumption, credits (always of water) accounted for and debts collected…The Chinese multinationals have exchanged the public debt of other states with their water reserves with which, now, they can control the climate, deciding when and where it will rain. Who understands this dirty game has been silenced, like Hilda’s mother, a limnologist, inexplicably arrested and never returned; like the daughter of two water vendors, mysteriously disappeared, after having decided not to bow to economic powers: Hanna, who now prefers secure virtual identities to evanescent real appearances. Water. The two, like the covalent bond of a complex molecule, develop a relationship of attraction and repulsion that will first make them meet and then, little by little, will change into a tormented love but, at the same time, so pure as to cause Hilda at great risk, to make an extreme decision that will allow Hanna to realize the strange prophecy that the internal voice, perhaps the consciousness of water, had resonated in the two women for a long time. “The Way of Water” will also appear alongside a collection of international works (including authors from Greece, Nigeria, China, India, Russia, Mexico, USA, UK, Italy, Canada (yours truly), Cuba, and Zimbabwe) in Bill Campbell and Francesco Verso’s
“The Way of Water” will also appear alongside a collection of international works (including authors from Greece, Nigeria, China, India, Russia, Mexico, USA, UK, Italy, Canada (yours truly), Cuba, and Zimbabwe) in Bill Campbell and Francesco Verso’s  After she and fellow colonists crash land on the hostile jungle planet of Mega, rebel-scientist Izumi, widower and hermit, boldly sets out against orders on a hunch that may ultimately save her fellow survivors—but may also risk all. As the other colonists take stock, Izumi—obsessed with discovery and the need to save lives—plunges into the dangerous forest, which harbors answers, not only to their freshwater problem, but ultimately to the nature of the universe itself. Mega was a goldilocks planet—it had saltwater and supported life—but the planet also possessed magnetic-electro-gravitational anomalies and a gravitational field that didn’t match its size and mass. The synchronous dance of its global electromagnetic field suggested self-organization to Izumi, who slowly pieced together Mega’s secrets: from its “honeycomb” pools to the six-legged uber-predators and jungle infrasounds—somehow all connected to the water. Still haunted by the meaningless death of her family back on Mars, Izumi’s intrepid search for life becomes a metaphoric and existential journey of the heart that explores how we connect and communicate—with one another and the universe—a journey intimately connected with water.
After she and fellow colonists crash land on the hostile jungle planet of Mega, rebel-scientist Izumi, widower and hermit, boldly sets out against orders on a hunch that may ultimately save her fellow survivors—but may also risk all. As the other colonists take stock, Izumi—obsessed with discovery and the need to save lives—plunges into the dangerous forest, which harbors answers, not only to their freshwater problem, but ultimately to the nature of the universe itself. Mega was a goldilocks planet—it had saltwater and supported life—but the planet also possessed magnetic-electro-gravitational anomalies and a gravitational field that didn’t match its size and mass. The synchronous dance of its global electromagnetic field suggested self-organization to Izumi, who slowly pieced together Mega’s secrets: from its “honeycomb” pools to the six-legged uber-predators and jungle infrasounds—somehow all connected to the water. Still haunted by the meaningless death of her family back on Mars, Izumi’s intrepid search for life becomes a metaphoric and existential journey of the heart that explores how we connect and communicate—with one another and the universe—a journey intimately connected with water. Fingal’s Cave
Fingal’s Cave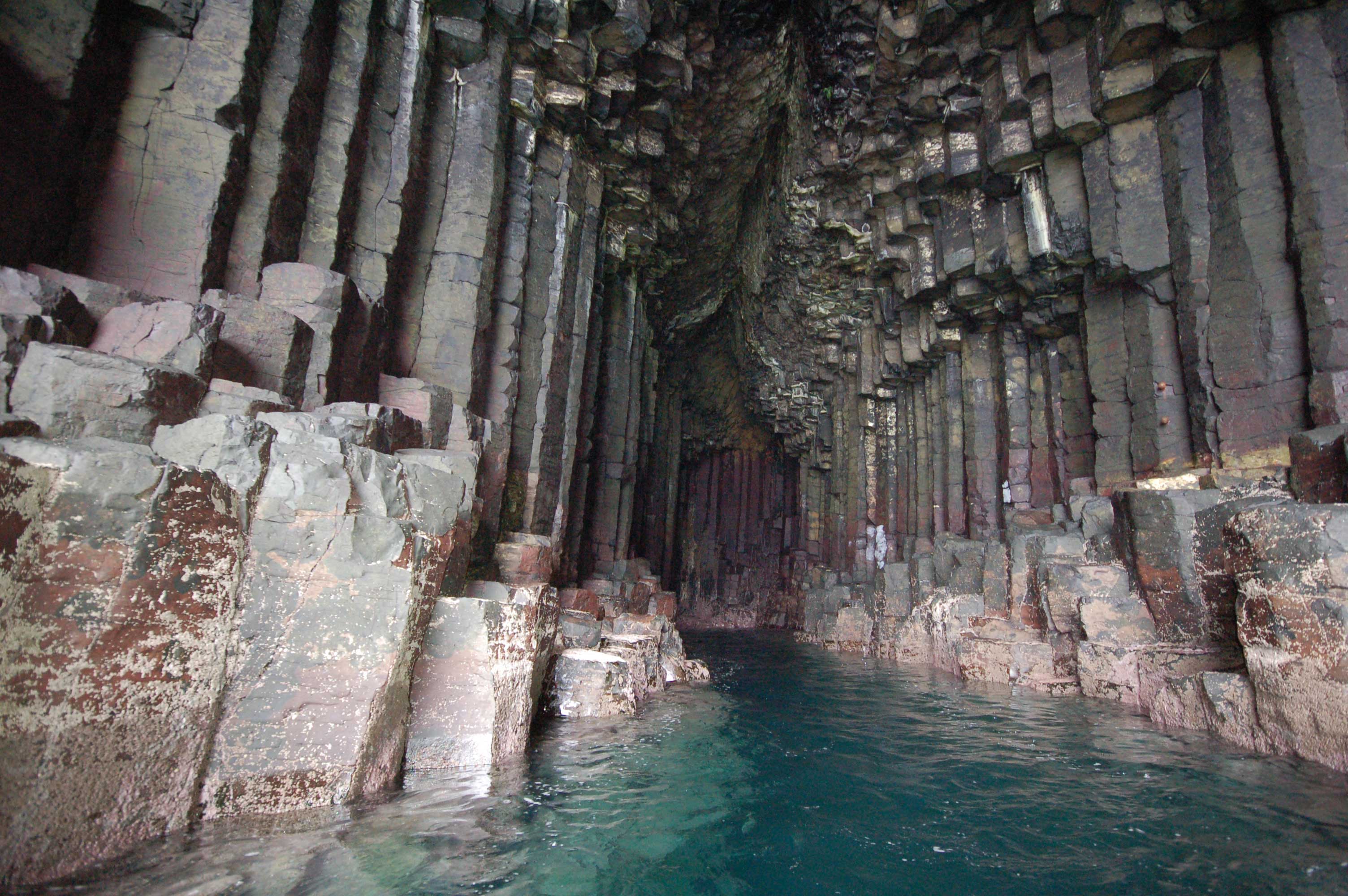 Fingal’s Cave is a sea cave on the uninhabited island of Staffa in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The cave is formed entirely from hexagonally jointed basalt columns in a Paleocene lava flow (similar to the Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland). Its entrance is a large archway filled by the sea. The eerie sounds made by the echoes of waves in the cave, give it the atmosphere of a natural cathedral. Known for its natural acoustics, the cave is named after the hero of an epic poem by 18th century Scots poet-historian James Macpherson. Fingal means “white stranger”.
Fingal’s Cave is a sea cave on the uninhabited island of Staffa in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The cave is formed entirely from hexagonally jointed basalt columns in a Paleocene lava flow (similar to the Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland). Its entrance is a large archway filled by the sea. The eerie sounds made by the echoes of waves in the cave, give it the atmosphere of a natural cathedral. Known for its natural acoustics, the cave is named after the hero of an epic poem by 18th century Scots poet-historian James Macpherson. Fingal means “white stranger”.


 In December 2017, “Water”, the first of Reality Skimming Press’s Optimistic Sci-Fi Series was released in Vancouver, BC. I was invited to be one of the editors for the anthology, given my passion for and experience with water.
In December 2017, “Water”, the first of Reality Skimming Press’s Optimistic Sci-Fi Series was released in Vancouver, BC. I was invited to be one of the editors for the anthology, given my passion for and experience with water.

 In the years that followed, Reality Skimming Press published several works, including the “Megan Survival” Anthology for which I wrote a short story, “
In the years that followed, Reality Skimming Press published several works, including the “Megan Survival” Anthology for which I wrote a short story, “

 Blika lived in Mossland with her clone sestras, gathering and sucking the delicious juices of detritus and algae. Never in a hurry, she lumbered from frond to frond on eight stubby legs in a gestalt of feasting and being. Blika led a microscopic life of bloated bliss—unaware of forests, human beings, quantum physics or the coming singularity…
Blika lived in Mossland with her clone sestras, gathering and sucking the delicious juices of detritus and algae. Never in a hurry, she lumbered from frond to frond on eight stubby legs in a gestalt of feasting and being. Blika led a microscopic life of bloated bliss—unaware of forests, human beings, quantum physics or the coming singularity…


 “Because we are ALL sestras! You are a Tardigrade, aren’t you?” She waved all eight arms at Blika. “Well, I am your queen!” She looked self-pleased. “You are in Tunland now! The land of awareness. And now that you are self-aware, you can do anything! We’re special,” the queen ended in smug delight. The folds of her body jiggled and shimmered.
“Because we are ALL sestras! You are a Tardigrade, aren’t you?” She waved all eight arms at Blika. “Well, I am your queen!” She looked self-pleased. “You are in Tunland now! The land of awareness. And now that you are self-aware, you can do anything! We’re special,” the queen ended in smug delight. The folds of her body jiggled and shimmered.
 They entered a strange place of giant blocks and whining sounds beneath a dark swirling sky.
They entered a strange place of giant blocks and whining sounds beneath a dark swirling sky. As if she knew what Blika wanted, the queen quickly added, “But you can never go back home!”
As if she knew what Blika wanted, the queen quickly added, “But you can never go back home!”
 The water came in a giant wet wave of blue and silver and frothy green. Tunland sloshed then totally dissolved. Blika surfed the churning water. That green! She knew what it was! Blika reached out with her deft claws and snagged a tumbling moss frond. It finally settled and there were her sestras! So many of them clinging to the same green moss! She’d found her family! She was home! Yes, it was a different home and different sestras, but it was also the same. Love made it so…
The water came in a giant wet wave of blue and silver and frothy green. Tunland sloshed then totally dissolved. Blika surfed the churning water. That green! She knew what it was! Blika reached out with her deft claws and snagged a tumbling moss frond. It finally settled and there were her sestras! So many of them clinging to the same green moss! She’d found her family! She was home! Yes, it was a different home and different sestras, but it was also the same. Love made it so… Tardigrades, also known as water bears or moss piglets, are plump, microscopic organisms with eight clawed legs. Fossils of tardigrades date to the Cambrian period over 500 million years ago. Over 900 species are known. Tardigrades were first described by the German pastor Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773 and given the name Tardigrada, meaning “slow stepper,” by the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani. Tardigrades reproduce asexually (parthenogenesis) or sexually. They mostly suck on the fluids of plant cells, animal cells, and bacteria.
Tardigrades, also known as water bears or moss piglets, are plump, microscopic organisms with eight clawed legs. Fossils of tardigrades date to the Cambrian period over 500 million years ago. Over 900 species are known. Tardigrades were first described by the German pastor Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773 and given the name Tardigrada, meaning “slow stepper,” by the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani. Tardigrades reproduce asexually (parthenogenesis) or sexually. They mostly suck on the fluids of plant cells, animal cells, and bacteria. Tardigrades respond to adverse environmental stresses through “cryptobiosis”, a process that greatly slows their metabolism. Tardigrades survive dry periods by shriveling up into a little ball or tun and waiting it out. They make a protective sugar called trehalose, which moves into the cells to replace the lost water. You could say that the water bear turns into a gummy bear.
Tardigrades respond to adverse environmental stresses through “cryptobiosis”, a process that greatly slows their metabolism. Tardigrades survive dry periods by shriveling up into a little ball or tun and waiting it out. They make a protective sugar called trehalose, which moves into the cells to replace the lost water. You could say that the water bear turns into a gummy bear. My Book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press explores this creature and many other interesting things about water. Look for it on Amazon, Chapters, Kobo and in bookstores & libraries near you. If it’s not in your local library, ask for it.
My Book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press explores this creature and many other interesting things about water. Look for it on Amazon, Chapters, Kobo and in bookstores & libraries near you. If it’s not in your local library, ask for it. Arizona State University’s Imagination and Climate Futures Initiative is again hosting a Climate Fiction Short Story Contest. In years past they invited writers from around the world to submit speculative fiction stories that explore climate change to narrate a world in flux. Previous contests received submissions from 67 different countries and 12 finalists were published in a digital anthology “Everything Change”.
Arizona State University’s Imagination and Climate Futures Initiative is again hosting a Climate Fiction Short Story Contest. In years past they invited writers from around the world to submit speculative fiction stories that explore climate change to narrate a world in flux. Previous contests received submissions from 67 different countries and 12 finalists were published in a digital anthology “Everything Change”.
