path along Credit River (photo by Nina Munteanu)
It was a while ago, as I was driving home from a friend’s place in the sultry dark of night that I noticed the change…
Perhaps it was the rain and the winding road that nudged my psyche to wander into that other realm. Or was it the surrealistic motion picture The Fountain that I’d seen the evening before? Or had it more to do with the fact that I’d been, for various reasons, without sleep for over forty hours that I glimpsed the ordinary in an extra-ordinary light?
Light had everything to do with it…Amber traffic lights at a construction site pulsed like living things. Smoky back-lit clouds billowed over an inky sky. A garish screen of trees, caught in the beams of my car lights as I turned a corner, flashed. Nature recast. A half-built apartment building loomed up like some dark tower in Lord of the Rings. I was reminded of a scene early on in The Fountain where the viewer is disoriented initially by a busy street at night because it was shot upside down. Ironically, the picture was filmed in my hometown of Montreal and I didn’t even recognize it.
Have you ever done that? Looked backward while driving through a familiar scene to gain a different perspective? And felt different for just a moment? Like you’d briefly entered a different dimension and glimpsed “the other”?
What is it like to meet “the other”?
What is it like to approach the unfamiliar? A new landscape. A stranger in town. A different culture. An “alien” encounter. How do we react? Is it with wonder? Curiosity? Fear? Hatred? A mixture of these?
The genre of science fiction vividly explores our humanity through our reactions to “the other.” It does this by looking at both perspectives. By describing “the other,” science fiction writers describe “us.” In his book Orientalism: Western Conceptions of the Orient Edward W. Said contended that for there to be an ‘us’, there has to be a ‘not-us.’ According to Patricia Kerslake of Central Queensland University, this arises from a postcolonial notion of ‘the Other’, through a mutual process of exclusion. This exclusion inspires the very idea of ‘alien’ by imposing expectation on perception. Kerslake argues that: “When one culture imposes its perceptions on another, in that it begins to see the Other not as they are but as, in Said’s words, ‘they ought to be’, then the process of representation becomes inevitable: a choice is made to see a ‘preferred’ real.”

Ursula K. LeGuin
In her 1975 article “American SF and the Other,” Ursula K. LeGuin unequivocally scolded the Western SF genre for representing and promoting colonialism and androcratic motives.
One of the great early socialists said that the status of women in a society is a pretty reliable index of the degree of civilization of that society. If this is true, then the very low status of women in SF should make us ponder about whether SF is civilized at all.
The women’s movement has made most of us conscious of the fact that SF has either totally ignored women, or presented them as squeaking dolls subject to instant rape by monsters—or old-maid scientists de-sexed by hypertrophy of the intellectual organs—or, at best, loyal little wives or mistresses of accomplished heroes. Male elitism has run rampant in SF. But is it only male elitism? Isn’t the “subjection of women” in SF merely a symptom of a whole which is authoritarian, power-worshiping, and intensely parochial?
The question involved here is the question of The Other—the being who is different from yourself. This being can be different from you in its sex; or in its annual income; or in its way of speaking and dressing and doing things; or in the color of its skin, or the number of its legs and heads. In other words, there is the sexual Alien, and the social Alien, and the cultural Alien, and finally the racial Alien.
Well, how about the social Alien in SF? How about, in Marxist terms, “the proletariat”? Where are they in SF? Where are the poor, the people who work hard and go to bed hungry? Are they ever persons, in SF? No. They appear as vast anonymous masses fleeing from giant slime-globules from the Chicago sewers, or dying off by the billion from pollution or radiation, or as faceless armies being led to battle by generals and statesmen. In sword and sorcery they behave like the walk-on parts in a high school performance of The Chocolate Prince. Now and then there’s a busty lass amongst them who is honored by the attentions of the Captain of the Supreme Terran Command, or in a space-ship crew there’s a quaint old cook, with a Scots or Swedish accent, representing the Wisdom of the Common Folk.
The people, in SF, are not people. They are masses, existing for one purpose: to be led by their superiors…
…What about the cultural and the racial Other? This is the Alien everybody recognizes as alien, supposed to be the special concern of SF. Well, in the old pulp SF, it’s very simple. The only good alien is a dead alien—whether he is an Aldebaranian Mantis-Man, or a German dentist. And this tradition still flourishes: witness Larry Niven’s story “Inconstant Moon” (in All the Myriad Ways, 1941) which has a happy ending—consisting of the fact that America, including Los Angeles, was not hurt by a solar flare. Of course a few million Europeans and Asians were fried, but that doesn’t matter, it just makes the world a little safer for democracy, in fact. (It is interesting that the female character in the same story is quite brainless; her only function is to say Oh? and Ooooh! to the clever and resourceful hero.)
If you deny any affinity with another person or kind of person, if you declare it to be wholly different from yourself—as men have done to women, and class has done to class, and nation has done to nation—you may hate it, or deify it; but in either case you have denied its spiritual equality, and its human reality. You have made it into a thing, to which the only possible relationship is a power relationship. And thus you have fatally impoverished your own reality.
You have, in fact, alienated yourself.
 Written 45 years ago, Le Guin’s scathing article may have accurately represented the North American science fiction community of writers of that time. Today, despite the remnants of a strong old guard that still promotes a patriarchal colonialist hegemony, the science fiction genre has matured and grown beyond this self-limiting view. This is partly because current authors—many who are women and many who are representatives of minority or marginalized groups—have given SF a new face and voice that promises to include equality, inclusion, and a fresh look at exploration and ‘the other.’
Written 45 years ago, Le Guin’s scathing article may have accurately represented the North American science fiction community of writers of that time. Today, despite the remnants of a strong old guard that still promotes a patriarchal colonialist hegemony, the science fiction genre has matured and grown beyond this self-limiting view. This is partly because current authors—many who are women and many who are representatives of minority or marginalized groups—have given SF a new face and voice that promises to include equality, inclusion, and a fresh look at exploration and ‘the other.’
The genre of science fiction has matured by diversifying to embrace “mundane science fiction,” literary fiction, speculative fiction, climate fiction, cli-fi, eco-fiction, indigenous futurisms and more.
 Science fiction that leans toward “mundane”(everyday life) and literary fiction include the works of Paulo Bacigalupi (Windup Girl), Margaret Atwood (Year of the Flood), and Kim Stanley Robinson (New York 2140). Literary fiction overlaps with science fiction through eco-fiction and climate fiction which address oppression, jingoism and neoliberalism often through dystopian themes—and often through the voice of women writers—such as Octavia Butler’s Parable of the Sower, N.K. Jemisin’s The Broken Earth series, Emmi Itäranta’s The Memory of Water, Nina Munteanu’s A Diary in the Age of Water, Barbara Kingsolver’s Flight Behavior, Annie Proulx’s Barkskins, and Richard Power’s Overstory.
Science fiction that leans toward “mundane”(everyday life) and literary fiction include the works of Paulo Bacigalupi (Windup Girl), Margaret Atwood (Year of the Flood), and Kim Stanley Robinson (New York 2140). Literary fiction overlaps with science fiction through eco-fiction and climate fiction which address oppression, jingoism and neoliberalism often through dystopian themes—and often through the voice of women writers—such as Octavia Butler’s Parable of the Sower, N.K. Jemisin’s The Broken Earth series, Emmi Itäranta’s The Memory of Water, Nina Munteanu’s A Diary in the Age of Water, Barbara Kingsolver’s Flight Behavior, Annie Proulx’s Barkskins, and Richard Power’s Overstory.
 In 2017, several publications addressed different aspects of society through speculative fiction. Laksa Media published Strangers Among Us: Tales of the Underdogs and Outcasts, which explores issues of mental health. Exile Editions published Cli-Fi: Tales of Climate Change with stories on personal experience with climate change. Reality Skimming Press published Water, for which I was editor, which explored optimism in the face of climate change.
In 2017, several publications addressed different aspects of society through speculative fiction. Laksa Media published Strangers Among Us: Tales of the Underdogs and Outcasts, which explores issues of mental health. Exile Editions published Cli-Fi: Tales of Climate Change with stories on personal experience with climate change. Reality Skimming Press published Water, for which I was editor, which explored optimism in the face of climate change.
In Ann Leckie’s 2014 Ancillary Justice, the main character is a space ship. The Gethenians in Ursula K. LeGuin’s The Left Hand of Darkness are humanoids with fluid gender, adapted to environment. In Kim Stanley Robinson’s 2312, humans have abandoned the gender binary for an intersex existence based on proven longevity.
 Novels and anthologies of short stories that feature disabled characters are also growing. Examples include Borderline by Mishell Baker, We Who Are About To… by Joanna Russ, Murderbot series by Martha Wells, and Uncanny: Disabled People Destroy Science Fiction (edited by Elsa Sjunneson-Henry, Dominik Parisien et al.) among many others.
Novels and anthologies of short stories that feature disabled characters are also growing. Examples include Borderline by Mishell Baker, We Who Are About To… by Joanna Russ, Murderbot series by Martha Wells, and Uncanny: Disabled People Destroy Science Fiction (edited by Elsa Sjunneson-Henry, Dominik Parisien et al.) among many others.
Indigenous futurisms, speculative writings on issues of colonialism, identity, AI, and climate change include Trail of Lightning by Rebecca Roanhorse, Mongrels by Stephen Graham Jones, Robopocalypse by Daniel H. Wilson, Take Us to Your Chief, by Drew Hayden Taylor, The Marrow Thieves by Cherie Dimaline, Walking the Clouds Anthology edited by Grace L. Dillon, and Future Home of the Living God by Louise Erdrich.
 In an introduction to seven Indigenous Futurism books, Barnes and Noble writes:
In an introduction to seven Indigenous Futurism books, Barnes and Noble writes:
So many stories, well intentioned and not-so-well-intentioned, have fixated on the dark pasts of Indigenous people, assuming that colonization stole from them any future not involving slow decline and assimilation. Though there’s plenty of tragedy to be recounted, Indigenous history didn’t end there, and a wave of modern authors are exploring Indigenous cultures as living, vibrant, and firmly fixed in both the modern and furute worlds—sovereign nations with as much claim to an endless array of possible futures as any other culture. So much of what we call classic science fiction involves tropes that look very different to colonized peoples: the heroic space explorers who travel the stars visiting (and often conquering) alien worlds look very different to people whose histories are so strongly marked by the scars of colonization.
Of Indigenous Futurisms, the Seattle Public Library writes:
Indigenous Futurisms confront many of the norms of speculative fiction by challenging, subverting, or refusing to engage with colonial, racist, and otherwise oppressive genre tropes. Indigenous Futurism draws on the strength of Indigenous knowledge systems, worldviews, stories, languages, and traditions to reimagine the past, present, and future of this world and others. Yet it is not necessarily utopic or optimistic. Many authors writing within the Indigenous Futurisms genre engage with the realities of ongoing colonialism around the world, and the apocalyptic nature of the present for many Indigenous communities. However, characters struggle despite the circumstances for a better future.

First snow on the Credit River (photo by Nina Munteanu)

Nina Munteanu is a Canadian ecologist / limnologist and novelist. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” was published by Mincione Edizioni in Rome. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press (Vancouver) was selected by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times ‘Year in Reading’ and was chosen as the 2017 Summer Read by Water Canada. Her novel “A Diary in the Age of Water” will be released by Inanna Publications (Toronto) in June 2020.























 *A version of this talk is available in an article I wrote called “Coming Home to Water,” which first appeared in the 2016 anthology In the Moment (A Hopeful Sign) edited by Gary Doi. It was reprinted in 2018 The Earth We Love (Mississauga Writers) edited by Elizabeth Banfalvi; and again in 2019 in The Literary Connection IV: Then and Now (IOWI) edited by Cheryl Antao Xavier.
*A version of this talk is available in an article I wrote called “Coming Home to Water,” which first appeared in the 2016 anthology In the Moment (A Hopeful Sign) edited by Gary Doi. It was reprinted in 2018 The Earth We Love (Mississauga Writers) edited by Elizabeth Banfalvi; and again in 2019 in The Literary Connection IV: Then and Now (IOWI) edited by Cheryl Antao Xavier.

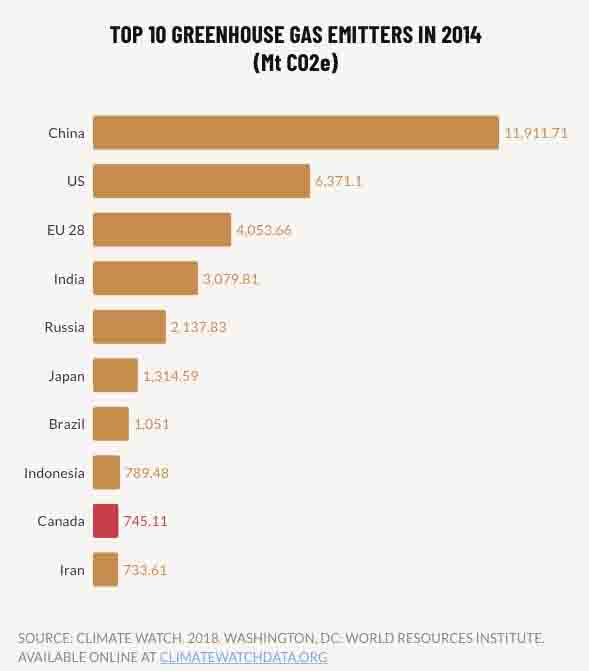
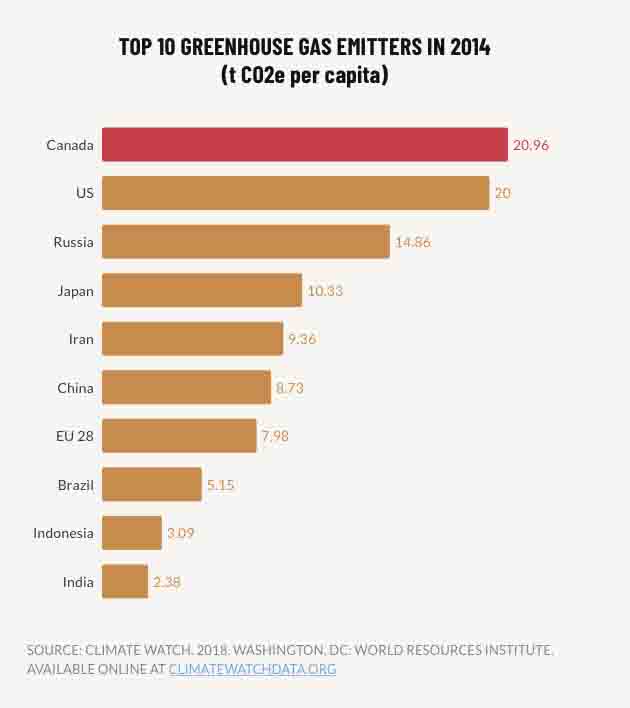
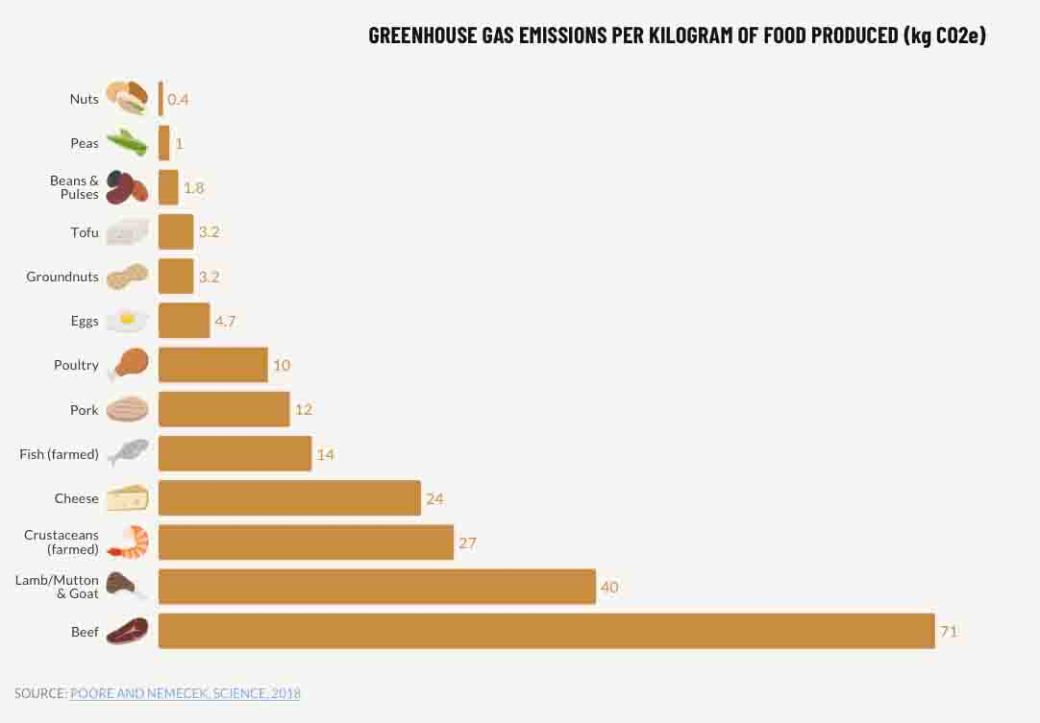




 Mapes reveals that her witness tree overcame a 1 in 500 chance of taking root from tiny acorn to seedling to become a thirteen-storey tall giant. Mapes considered her oak a living timeline that revealed through its phenology how climate change is resetting the seasonal clock.
Mapes reveals that her witness tree overcame a 1 in 500 chance of taking root from tiny acorn to seedling to become a thirteen-storey tall giant. Mapes considered her oak a living timeline that revealed through its phenology how climate change is resetting the seasonal clock. 

 Written with passionate lyricism and a mother’s nurturing spirit, Irish storyteller Beresford-Kroeger weaves a compelling tapestry of ancient forest lore with modern science to promote the global forest. Tapping into aboriginal wisdom and ancient pagan legend, Beresford-Kroeger invites you into the forest to explore the many beneficial and pharmaceutical properties of trees—from leaves that filter the air of particulate pollution, the cardiotonic property of hawthorn, fatty acids in hickory nuts and walnuts that promote brain development, to the aerosols in pine trees that calm nerves.
Written with passionate lyricism and a mother’s nurturing spirit, Irish storyteller Beresford-Kroeger weaves a compelling tapestry of ancient forest lore with modern science to promote the global forest. Tapping into aboriginal wisdom and ancient pagan legend, Beresford-Kroeger invites you into the forest to explore the many beneficial and pharmaceutical properties of trees—from leaves that filter the air of particulate pollution, the cardiotonic property of hawthorn, fatty acids in hickory nuts and walnuts that promote brain development, to the aerosols in pine trees that calm nerves.

 In his travels to visit iconic trees around the world, Haskell draws on the wisdom and moral ethics of “ecological aesthetics” to describe a natural beauty—not as individual property but as a world within a world of interactive life to which we belong and serve but do not own:
In his travels to visit iconic trees around the world, Haskell draws on the wisdom and moral ethics of “ecological aesthetics” to describe a natural beauty—not as individual property but as a world within a world of interactive life to which we belong and serve but do not own:


 Olivia Vandergriff miraculously survives an electrocution to become an ecowarrior after she begins to hear the voices of the trees. She rallies others to embrace the urgency of activism in fighting the destruction of California’s redwoods and even camps in the canopy of one of the trees to deter the logging. When the ancient tree she has unsuccessfully protected is felled, the sound is “like an artillery shell hitting a cathedral.” Vandergriff weeps for this magnificent thousand-year old tree. So do I. Perhaps the real heroes of this novel are the ancient trees.
Olivia Vandergriff miraculously survives an electrocution to become an ecowarrior after she begins to hear the voices of the trees. She rallies others to embrace the urgency of activism in fighting the destruction of California’s redwoods and even camps in the canopy of one of the trees to deter the logging. When the ancient tree she has unsuccessfully protected is felled, the sound is “like an artillery shell hitting a cathedral.” Vandergriff weeps for this magnificent thousand-year old tree. So do I. Perhaps the real heroes of this novel are the ancient trees.

 Proulx immerses the reader in rich sensory detail of a place and time, equally comfortable describing a white pine stand in Michigan and logging camp in Upper Gatineau to a Mi’kmaq village on the Nova Scotia coast or the stately Boston home of Charles Duquet. The foreshadowing of doom for the magnificent forests is cast by the shadow of how settlers treat the Mi’kmaq people. The fate of the forests and the Mi’kmaq are inextricably linked through settler disrespect and a fierce hunger for “more.”
Proulx immerses the reader in rich sensory detail of a place and time, equally comfortable describing a white pine stand in Michigan and logging camp in Upper Gatineau to a Mi’kmaq village on the Nova Scotia coast or the stately Boston home of Charles Duquet. The foreshadowing of doom for the magnificent forests is cast by the shadow of how settlers treat the Mi’kmaq people. The fate of the forests and the Mi’kmaq are inextricably linked through settler disrespect and a fierce hunger for “more.”


 I recently gave a 2-hour workshop on “ecology of story” at Calgary’s
I recently gave a 2-hour workshop on “ecology of story” at Calgary’s 






 Nina is a Canadian scientist and novelist. She worked for 25 years as an environmental consultant in the field of aquatic ecology and limnology, publishing papers and technical reports on water quality and impacts to aquatic systems. Nina has written over a dozen eco-fiction, science fiction and fantasy novels. An award-winning short story writer, and essayist, Nina currently lives in Toronto where she teaches writing at the University of Toronto and George Brown College. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…”—a scientific study and personal journey as limnologist, mother, teacher and environmentalist—was picked by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times as 2016 ‘The Year in Reading’. Nina’s most recent novel “A Diary in the Age of Water”— about four generations of women and their relationship to water in a rapidly changing world—will be released in 2020 by Inanna Publications.
Nina is a Canadian scientist and novelist. She worked for 25 years as an environmental consultant in the field of aquatic ecology and limnology, publishing papers and technical reports on water quality and impacts to aquatic systems. Nina has written over a dozen eco-fiction, science fiction and fantasy novels. An award-winning short story writer, and essayist, Nina currently lives in Toronto where she teaches writing at the University of Toronto and George Brown College. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…”—a scientific study and personal journey as limnologist, mother, teacher and environmentalist—was picked by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times as 2016 ‘The Year in Reading’. Nina’s most recent novel “A Diary in the Age of Water”— about four generations of women and their relationship to water in a rapidly changing world—will be released in 2020 by Inanna Publications. “By failing to engage with climate change, artists and writers are contributing to an impoverished sense of the world, right at the moment when art and literature are most needed to galvanize a grassroots movement in favor of climate justice and carbon mitigation.”—Amitav Ghosh, 2017
“By failing to engage with climate change, artists and writers are contributing to an impoverished sense of the world, right at the moment when art and literature are most needed to galvanize a grassroots movement in favor of climate justice and carbon mitigation.”—Amitav Ghosh, 2017 What these novels have in common is that they are all
What these novels have in common is that they are all  According to Ghosh, plots and characters of contemporary literature tend to reflect the regularity of middle-class life and the worldview of the Victorian natural sciences, one that depends on a principle of uniformity. Change in Nature has been perceived as gradual (or static by some) and never catastrophic. Extraordinary or bizarre happenings were left to marginal genres like the Gothic tale and—of course—science fiction. The strange and unlikely have been externalized: hence the failure of modern novels and art to recognize anthropogenic climate change.
According to Ghosh, plots and characters of contemporary literature tend to reflect the regularity of middle-class life and the worldview of the Victorian natural sciences, one that depends on a principle of uniformity. Change in Nature has been perceived as gradual (or static by some) and never catastrophic. Extraordinary or bizarre happenings were left to marginal genres like the Gothic tale and—of course—science fiction. The strange and unlikely have been externalized: hence the failure of modern novels and art to recognize anthropogenic climate change.
 “To counteract this epidemic of short-term thinking,” says Fabiani, “it might be a good idea for more of us to read science fiction, specifically the post-apocalyptic sub-genre: that is, fiction dealing with the aftermath of major societal collapse, whether due to a pandemic, nuclear fallout, or climate change.”
“To counteract this epidemic of short-term thinking,” says Fabiani, “it might be a good idea for more of us to read science fiction, specifically the post-apocalyptic sub-genre: that is, fiction dealing with the aftermath of major societal collapse, whether due to a pandemic, nuclear fallout, or climate change.” I recently shared a panel discussion with writer
I recently shared a panel discussion with writer  In 2015, I joined Lynda Williams of Reality Skimming Press in creating an optimistic science fiction anthology with the theme of water. My foreword to
In 2015, I joined Lynda Williams of Reality Skimming Press in creating an optimistic science fiction anthology with the theme of water. My foreword to 

 In my new writing guidebook
In my new writing guidebook 
 In Animal Farm, George Orwell uses animals to describe the revolution against a totalitarian regime (e.g. the overthrow of the last Russian Csar and the Communist Revolution of Russia). The animals embrace archetypes to symbolize the actions and thoughts of various sectors within that world. The pigs are the leaders of the revolution; Mr. Jones represents the ruling despot who is overthrown; the horse Boxer is the ever-loyal and unquestioning labor class.
In Animal Farm, George Orwell uses animals to describe the revolution against a totalitarian regime (e.g. the overthrow of the last Russian Csar and the Communist Revolution of Russia). The animals embrace archetypes to symbolize the actions and thoughts of various sectors within that world. The pigs are the leaders of the revolution; Mr. Jones represents the ruling despot who is overthrown; the horse Boxer is the ever-loyal and unquestioning labor class. In Lord of the Flies, William Golding explores the conflict in humanity between the impulse toward civilization and the impulse toward savagery. The symbols of the island, the ocean, the conch shell, Piggy’s glasses, and the Lord of the Flies, or the Beast, represent central ideas that reinforce this main theme. Each character has recognizable symbolic significance: Ralph represents civilization and democracy; Piggy represents intellect and rationalism; Jack represents self-interested savagery and dictatorship; and Simon (the outsider in so many ways) represents altruistic purity.
In Lord of the Flies, William Golding explores the conflict in humanity between the impulse toward civilization and the impulse toward savagery. The symbols of the island, the ocean, the conch shell, Piggy’s glasses, and the Lord of the Flies, or the Beast, represent central ideas that reinforce this main theme. Each character has recognizable symbolic significance: Ralph represents civilization and democracy; Piggy represents intellect and rationalism; Jack represents self-interested savagery and dictatorship; and Simon (the outsider in so many ways) represents altruistic purity. Excellent examples of satires with less obvious allegorical structure (but it’s there) can be found in the genre of science fiction—a highly metaphorical literature that makes prime use of place and setting with archetypal characters to satirize an aspect of society. Brave New World by Aldous Huxley is a satirical response to his observation of humans’ addiction to (sexual) pleasure and vulnerability to mind control and the dumbing of civilization in the 1930s. George Orwell’s Nineteen Eight-Four satirizes humanity’s vulnerability to fascism, based on his perception of humans’ sense of fear and helplessness under powerful governments and their oppressive surveillance. Margaret Atwood’s The Handmaid’s Tale satirizes a society in which a woman struggles in a fundamentalist Christian dictatorship patriarchy where women are forced into a system of sexual slavery for the ruling patriarchy.
Excellent examples of satires with less obvious allegorical structure (but it’s there) can be found in the genre of science fiction—a highly metaphorical literature that makes prime use of place and setting with archetypal characters to satirize an aspect of society. Brave New World by Aldous Huxley is a satirical response to his observation of humans’ addiction to (sexual) pleasure and vulnerability to mind control and the dumbing of civilization in the 1930s. George Orwell’s Nineteen Eight-Four satirizes humanity’s vulnerability to fascism, based on his perception of humans’ sense of fear and helplessness under powerful governments and their oppressive surveillance. Margaret Atwood’s The Handmaid’s Tale satirizes a society in which a woman struggles in a fundamentalist Christian dictatorship patriarchy where women are forced into a system of sexual slavery for the ruling patriarchy. This article is an excerpt from “
This article is an excerpt from “

 She is inhumanly alone. And then, all at once, she isn’t. A beautiful animal stands on the other side of the water. They look up from their lives, woman and animal, amazed to find themselves in the same place. He freezes, inspecting her with his black-tipped ears. His back is purplish-brown in the dim light, sloping downward from the gentle hump of his shoulders. The forest’s shadows fall into lines across his white-striped flanks. His stiff forelegs play out to the sides like stilts, for he’s been caught in the act of reaching down for water. Without taking his eyes from her, he twitches a little at the knee, then the shoulder, where a fly devils him. Finally he surrenders his surprise, looks away, and drinks. She can feel the touch of his long, curled tongue on the water’s skin, as if he were lapping from her hand. His head bobs gently, nodding small, velvet horns lit white from behind like new leaves.
She is inhumanly alone. And then, all at once, she isn’t. A beautiful animal stands on the other side of the water. They look up from their lives, woman and animal, amazed to find themselves in the same place. He freezes, inspecting her with his black-tipped ears. His back is purplish-brown in the dim light, sloping downward from the gentle hump of his shoulders. The forest’s shadows fall into lines across his white-striped flanks. His stiff forelegs play out to the sides like stilts, for he’s been caught in the act of reaching down for water. Without taking his eyes from her, he twitches a little at the knee, then the shoulder, where a fly devils him. Finally he surrenders his surprise, looks away, and drinks. She can feel the touch of his long, curled tongue on the water’s skin, as if he were lapping from her hand. His head bobs gently, nodding small, velvet horns lit white from behind like new leaves.  An oligotrophic lake is basically a young lake. Still immature and undeveloped, an oligotrophic lake often displays a rugged untamed beauty. An oligotrophic lakes hungers for the stuff of life. Sediments from incoming rivers slowly feed it with dissolved nutrients and particulate organic matter. Detritus and associated microbes slowly seed the lake. Phytoplankton eventually flourish, food for zooplankton and fish. The shores then gradually slide and fill, as does the very bottom. Deltas form and macrophytes colonize the shallows. Birds bring in more creatures. And so on. Succession is the engine of destiny and trophic status its shibboleth.
An oligotrophic lake is basically a young lake. Still immature and undeveloped, an oligotrophic lake often displays a rugged untamed beauty. An oligotrophic lakes hungers for the stuff of life. Sediments from incoming rivers slowly feed it with dissolved nutrients and particulate organic matter. Detritus and associated microbes slowly seed the lake. Phytoplankton eventually flourish, food for zooplankton and fish. The shores then gradually slide and fill, as does the very bottom. Deltas form and macrophytes colonize the shallows. Birds bring in more creatures. And so on. Succession is the engine of destiny and trophic status its shibboleth. 
 They met in the lobby of a shabby downtown Toronto hotel. Hilda barely knew what she looked like but when Hanna entered the lobby through the front doors, Hilda knew every bit of her. Hanna swept in like a stray summer rainstorm, beaming with the self- conscious optimism of someone who recognized a twin sister. She reminded Hilda of her first boyfriend, clutching flowers in one hand and chocolate in the other. When their eyes met, Hilda knew. For an instant, she knew all of Hanna. For an instant, she’d glimpsed eternity. What she didn’t know then was that it was love.
They met in the lobby of a shabby downtown Toronto hotel. Hilda barely knew what she looked like but when Hanna entered the lobby through the front doors, Hilda knew every bit of her. Hanna swept in like a stray summer rainstorm, beaming with the self- conscious optimism of someone who recognized a twin sister. She reminded Hilda of her first boyfriend, clutching flowers in one hand and chocolate in the other. When their eyes met, Hilda knew. For an instant, she knew all of Hanna. For an instant, she’d glimpsed eternity. What she didn’t know then was that it was love.  This article is an excerpt from
This article is an excerpt from