Story is place, and place is character—Nina Munteanu
 I write mostly eco-fiction. Even before it was known as eco-fiction, I was writing it. My first book—Darwin’s Paradox—published in 2007 by Dragon Moon Press as science fiction, was also eco-fiction. It takes place in 2075 after climate change has turned southern Ontario into a heathland and Toronto into a self-enclosed city. My latest eco-fiction—A Diary in the Age of Water published in 2020 by Inanna Publications—is set mostly in Toronto from the near-future to 2065 and beyond.
I write mostly eco-fiction. Even before it was known as eco-fiction, I was writing it. My first book—Darwin’s Paradox—published in 2007 by Dragon Moon Press as science fiction, was also eco-fiction. It takes place in 2075 after climate change has turned southern Ontario into a heathland and Toronto into a self-enclosed city. My latest eco-fiction—A Diary in the Age of Water published in 2020 by Inanna Publications—is set mostly in Toronto from the near-future to 2065 and beyond.
As a writer of eco-fiction and climate fiction, I’m keenly aware of the role environment plays in story. Setting and place are often subtle yet integral aspects of story. In eco-fiction, they can even be a “character,” serve as archetypes and present metaphoric connections to characters on a journey (see my guidebook The Ecology of Story: World as Character published by Pixl Press for more discussion on all aspects of nature’s symbols in writing).
 Things to consider about place as character begin with the POV character and how they interact with their environment and how they reflect their place. For instance, is that interaction obvious or subtle? Is that environment constant or changing, stable or unstable, predictable, or variable? Is the place controllable or not, understandable or not? Is the relationship emotional, connected to senses such as memory?
Things to consider about place as character begin with the POV character and how they interact with their environment and how they reflect their place. For instance, is that interaction obvious or subtle? Is that environment constant or changing, stable or unstable, predictable, or variable? Is the place controllable or not, understandable or not? Is the relationship emotional, connected to senses such as memory?
Place as character serves as an archetype that story characters connect with and navigate in ways that depend on the theme of the story. A story’s theme is essentially the “so what part” of the story. What is at stake for the character on their journey. Theme is the backbone—the heart—of the story, driving characters to journey through time and place toward some kind of fulfillment. There is no story without theme. And there is no theme without place.
Archetypes are ancient patterns of personality shared universally by humanity (e.g. the “mother” archetype is recognized by all cultures). When place or aspects of place act as an archetype or symbol in story—particularly when linked to theme—this provides a depth of meaning that resonates through many levels for the reader.
In Ray Bradbury’s The Martian Chronicles, Mars symbolizes a new Eden. Like Bradbury’s aboriginal Martians—who are mostly invisible—the planet is a mirror that reflects humanity’s best and worst. Who we are, what we are, what we bring with us and what we may become. What we inadvertently do—to others, and finally to ourselves—and how the irony of chance can change everything.
“Nature’s symbols are powerful archetypes that reveal compelling story,” writes Donald Maass in Write the Breakout Novel Workbook.
 Water has been used as a powerful archetype in many novels. In my latest novel, A Diary in the Age of Water, water plays an important role through its unique metaphoric connection with each of the four main characters; how they relate to it and understand it, and act on its behalf. Water in A Diary in the Age of Water is often personified; water reflects various symbolic and allegorical interpretations and embraces several archetypes including herald-catalyst, trickster, shapeshifter, and shadow.
Water has been used as a powerful archetype in many novels. In my latest novel, A Diary in the Age of Water, water plays an important role through its unique metaphoric connection with each of the four main characters; how they relate to it and understand it, and act on its behalf. Water in A Diary in the Age of Water is often personified; water reflects various symbolic and allegorical interpretations and embraces several archetypes including herald-catalyst, trickster, shapeshifter, and shadow.
Strong relationships and linkages can be forged in story between a major character and an aspect of their environment (e.g., home/place, animal/pet, minor character as avatar/spokesperson for environment).
 In these examples the environmental aspect serves as symbol and metaphoric connection to theme. They can illuminate through the sub-text of metaphor a core aspect of the main character and their journey: the grounding nature of the land of Tara for Scarlet O’Hara in Margaret Mitchel’s Gone With the Wind; the white pine forests for the Mi’kmaq in Annie Proulx’s Barkskins; The animals for Beatrix Potter of the Susan Wittig Albert series.
In these examples the environmental aspect serves as symbol and metaphoric connection to theme. They can illuminate through the sub-text of metaphor a core aspect of the main character and their journey: the grounding nature of the land of Tara for Scarlet O’Hara in Margaret Mitchel’s Gone With the Wind; the white pine forests for the Mi’kmaq in Annie Proulx’s Barkskins; The animals for Beatrix Potter of the Susan Wittig Albert series.
All characters—whether the main POV character, or a minor character or personified element of the environment—have a dramatic function in your story. In my writing courses at George Brown College and The University of Toronto and in my guidebook The Fiction Writer, I provide a list of questions you can ask your character to determine if they are functioning well in the story and if they should even stay in the story. I call it interviewing your character. You can interview any character in your story; it can provide incredible insight. And speaking of character…
I have of late been walking daily to a lovely meadow beside a stream and thicket where brilliant Bull thistles have burst into flower. I felt the need to research this beautiful yet dangerously prickly plant and why it peaked my interest…
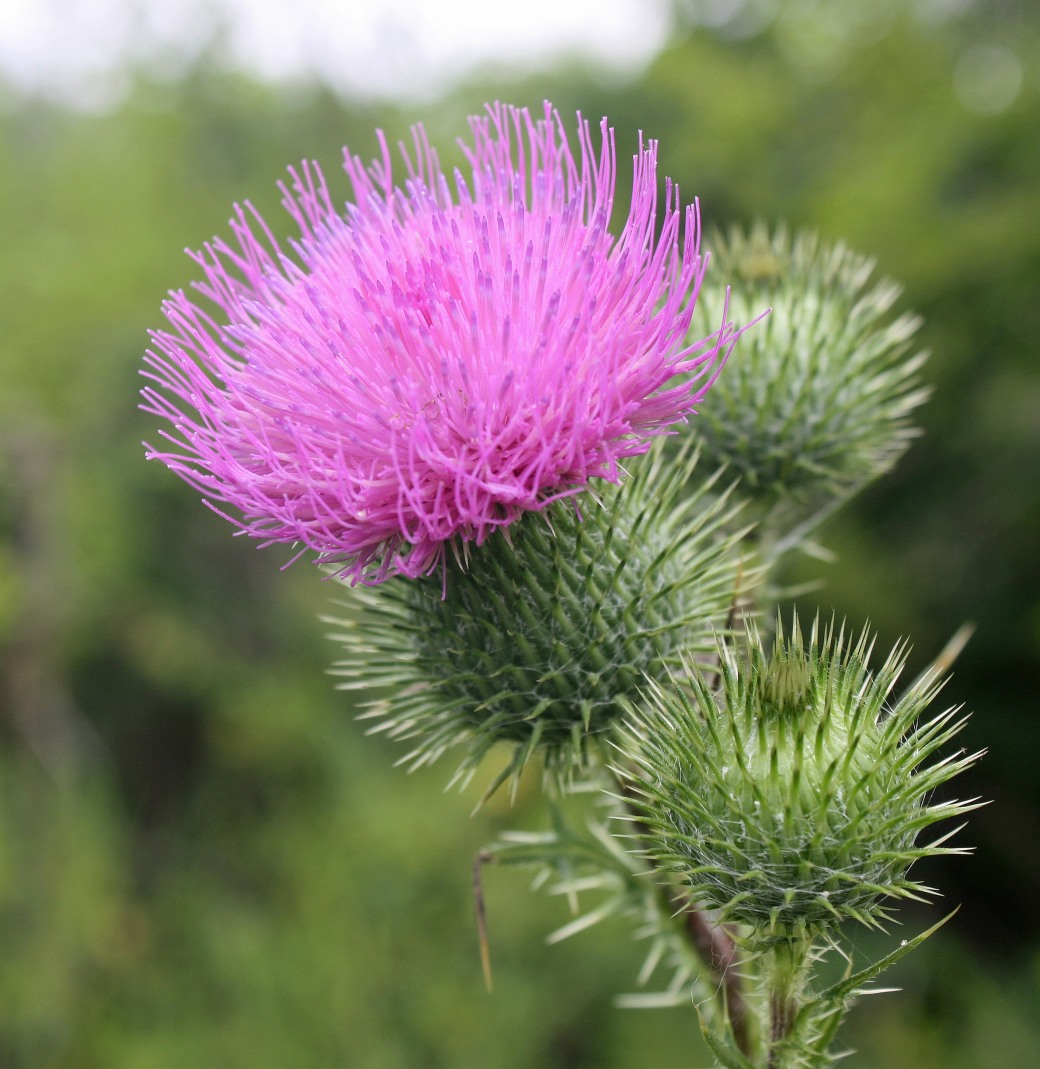

Bull Thistle, ON (photo by Nina Munteanu)
Interview With the Bull Thistle
Nina: Pardon my saying, but you seem to scream paradox. You’re dangerously beautiful. Alluring yet aloof. Standoffish, even threatening. For instance, how is it that you have such a beautiful single purple-pink flower at the top of such a nasty prickly stem and leaves?
Bull Thistle: First of all, it isn’t just a flower at the top; it’s a flower head of over two hundred flowers called florets. Each flower head is a tight community of tube disk bisexual florets arranged in Fibonacci spirals and protected by a collection of spiked bracts called an involucre. And inside the protective outer shell, embedded in a fleshy domed receptacle, are the tiny ovaries, waiting patiently to be fertilized and grown into a seed or achene.

Honey bee getting nectar from the thistle flower head (photo by Nina Munteanu)
Nina: Ah, I beg your pardon. But you still have all those sharp spikes everywhere. I’m guessing they are to protect your developing young, the ovaries. But doesn’t that isolate you? Keep you from integrating in your ecosystem?
Bull Thistle: The bristles are specifically aimed at predators who wish to harm us, eat us, bore into us, pull us out of the earth. We have many friends—the pollinators, the bees, wasps, and butterflies that help us cross-pollinate from plant to plant. And the birds—particularly the goldfinches—also help.
Nina: Wait. Don’t goldfinches eat your babies—eh, seeds?
Bull Thistle: They do. But they also help disperse our children. They land on our dried involucres—now opened to reveal the seeds and their pappus. The birds pull the seeds out by the thistle down that rides the wind. The birds eat the seeds and also use the thistle down to make their nests. But—like the squirrels who love oak acorns—the birds miss as many as they eat. By carrying the down to their nests, they also help the seeds travel great distances farther than the wind would have carried them. By dislodging the seeds in bunches, they help the seeds break away from the receptacle and meet the wind. The pappus, which is branched and light like a billowing sail, carries the seed on the wind to germinate elsewhere to help us colonize.
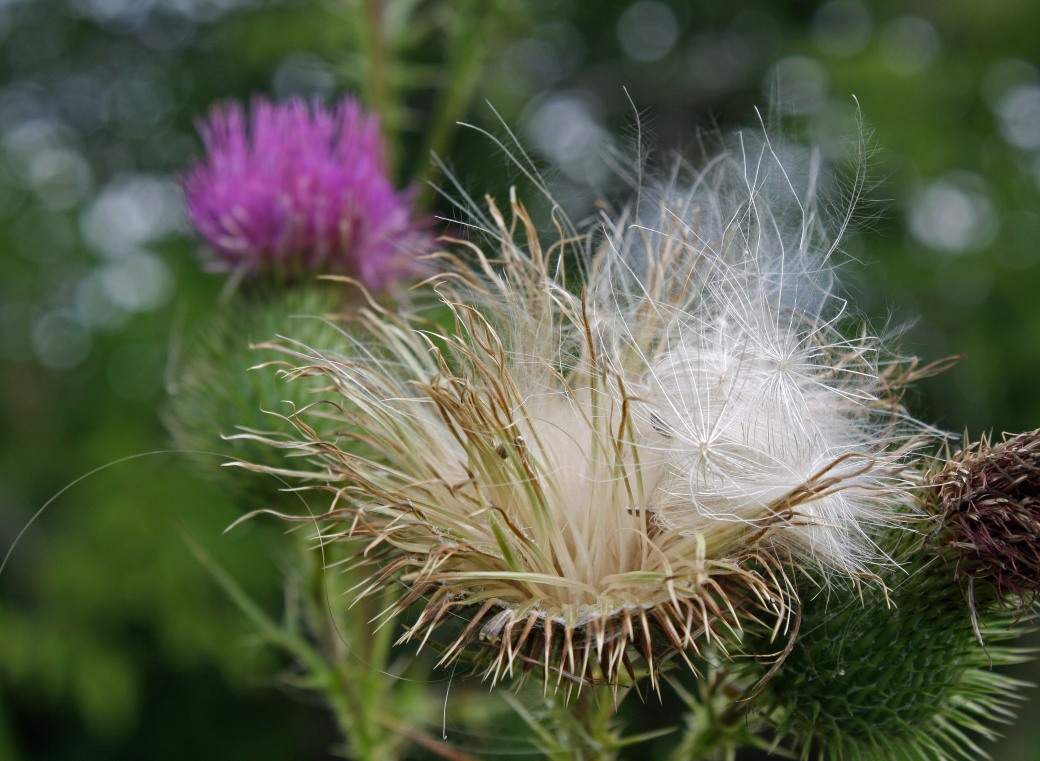

Opened involucre with achenes and pappus ready to disperse, ON (photo by Nina Munteanu)
Nina: So, your enemy is also your friend… The shadow character, who helps the hero on her journey by presenting a perilous aspect of enlightenment.
Bull Thistle: If you say so. What we understand is that Nature’s resilience derives from the balance of give and take over time. Prey and predator. Death, decay, transcendence. Destruction and creation. Ecological succession and change are a gestalt expression of Gaia wisdom as each individual fulfills its particular existential niche. Even if that is to die…for others to live.
Nina: Yes, the hero’s journey…But you’re not originally from here, are you? You were brought to North America from Eurasia. Some consider you an interloper, a disturbance. You could serve the shadow or trickster archetype yourself—outcompeting the native thistle, creating havoc with pasture crops. You can tolerate adverse environmental conditions and adapt to different habitats, letting you spread to new areas. Your high seed production, variation in dormancy, and vigorous growth makes you a serious invader. You cause wool fault and physical injury to animals. Storytellers might identify you metaphorically with the European settler in the colonialism of North America; bullying your way in and destroying the natives’ way of life.
Bull Thistle: We’re unaware of these negative things. We don’t judge. We don’t bully; we simply proliferate. We ensure the survival of our species through adaptation. Perhaps we do it better than others. You’ve lately discovered something we’ve felt and acted on for a long time. Climate is changing. We must keep up with the times… But to address your original challenge, if you did more research, you would find that we serve as superior nectar sources for honey bees (Apis spp.), bumblebees (Bombus spp.) and sweat bees (Anastogapus spp.) who thoroughly enjoy our nectar.

Sweat bee draws the sweet nectar of the Bull Thistle, ON (photo by Nina Munteanu)
We’re considered a top producer of nectar sugar in Britain. Cirsium vulgare—our official name—has ranked in the top 10 for nectar production in a recent UK survey. The goldfinch relies on our seed and down. And we’ve provided food, tinder, paper, and medicine to humans for millennia. As some of your indigenous people point out, it’s a matter of attitude. Change is opportunity.
 Nina: I guess that every weed was once a native somewhere. I also agree that times are changing—faster than many of us are ready for, humans included. If you were to identify with an archetype, which would you choose?
Nina: I guess that every weed was once a native somewhere. I also agree that times are changing—faster than many of us are ready for, humans included. If you were to identify with an archetype, which would you choose?
Bull Thistle: That would depend on the perceiver, we suppose. Some of us think of us as the hero, journeying through the change and struggling to survive; others see us as the herald, inciting movement and awareness by our very existence; some of us identify with the trickster, others with the shapeshifter—given how misunderstood we are. In the end, perhaps, we are the mentor, who provides direction through a shifting identity and pointing the way forward through the chaos of change toward enlightenment.
Nina: Yes, I suppose if someone stumbled into your nest of prickles, incredible awareness would result. Speaking of that very awareness, this brings me back to my original question: why are you so beautiful yet deadly?
Bull Thistle: We are the purest beauty—only attained through earnest and often painful awareness. We are the future and the beauty of things to come.
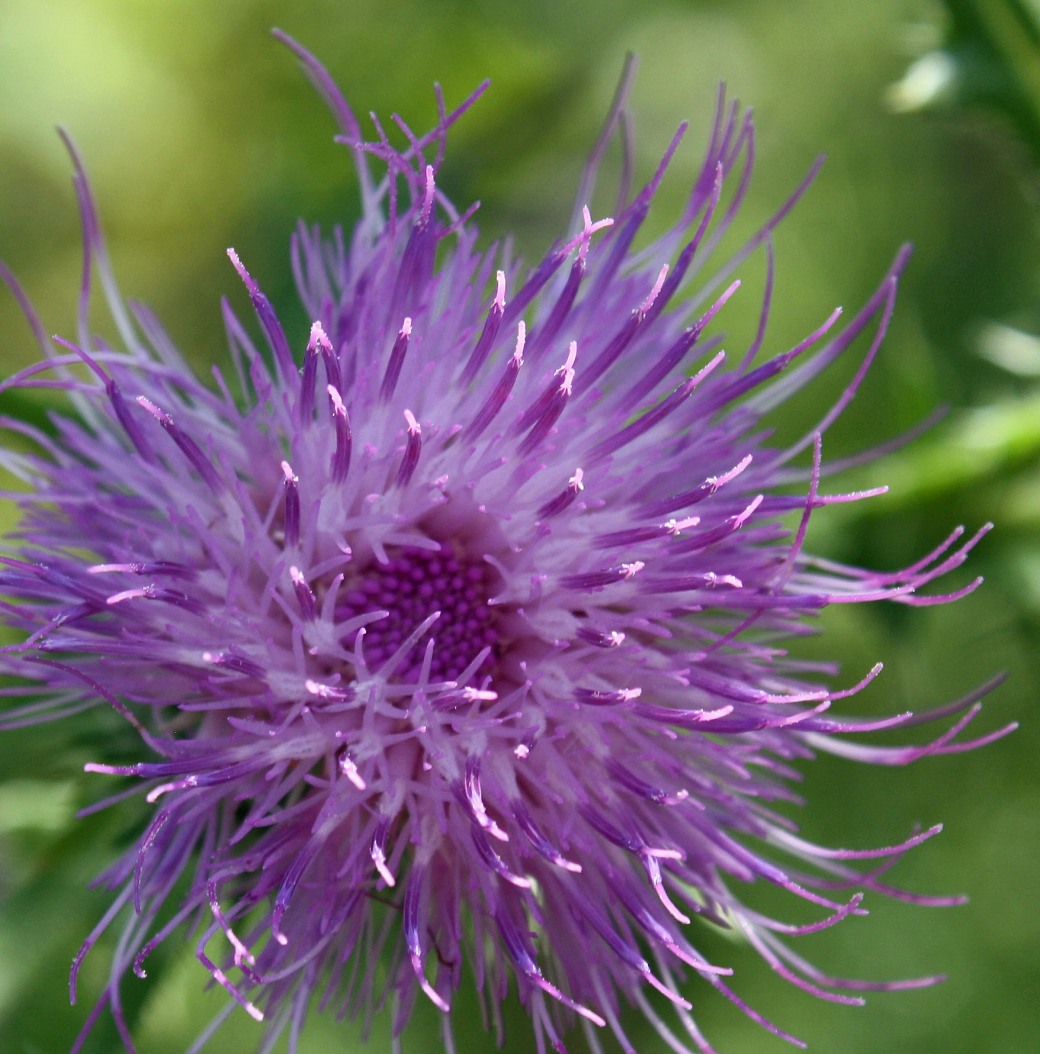

Flower head of Bull Thistle, ON (photo by Nina Munteanu)
You can read more on this topic in Nina’s writing guidebook series, particularly The Fiction Writer: Get Published, Write Now! and The Ecology of Story: World as Character.
Relevant Articles:
The Ecology of Story: Revealing Hidden Characters of the Forest
Ecology of Story: World as Character” Workshop at When Words Collide
Ecology of Story: Place as Allegory
Ecology of Story: Place as Symbol
Ecology of Story: Place as Metaphor
Ecology of Story: Place as Character & Archetype

Nina Munteanu is a Canadian ecologist / limnologist and novelist. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” was published by Mincione Edizioni in Rome. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press(Vancouver) was selected by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times ‘Year in Reading’ and was chosen as the 2017 Summer Read by Water Canada. Her novel “A Diary in the Age of Water” was released by Inanna Publications (Toronto) in June 2020.




 If you think this is all too weird, consider the weirdness of quantum mechanics, which shows us that not only is “solid” matter made up mostly of energy and “empty” space but what makes a solid a chair vs. you sitting on it is the vibration of its energy. Quantum science has demonstrated that light and matter are made of both particles and waves (New Scientist, May 6, 2010) and can exist in two simultaneous states. Let’s consider, for instance, “entanglement” (quantum non-local connection), the notion that particles can be linked in such a way that changing the quantum state of one instantaneously affects the other, even if they are light years apart. And what does it mean when solid flows, ghost-like, through itself under certain conditions? Or parallel universes created by splitting realities? Check out my historical fantasy novel
If you think this is all too weird, consider the weirdness of quantum mechanics, which shows us that not only is “solid” matter made up mostly of energy and “empty” space but what makes a solid a chair vs. you sitting on it is the vibration of its energy. Quantum science has demonstrated that light and matter are made of both particles and waves (New Scientist, May 6, 2010) and can exist in two simultaneous states. Let’s consider, for instance, “entanglement” (quantum non-local connection), the notion that particles can be linked in such a way that changing the quantum state of one instantaneously affects the other, even if they are light years apart. And what does it mean when solid flows, ghost-like, through itself under certain conditions? Or parallel universes created by splitting realities? Check out my historical fantasy novel 









 We are now living in the Age of Water. Water is the new “gold”, with individuals, corporations and countries positioning themselves around this precious resource. Water is changing everything. The Age of Water Podcast covers anything of interest from breaking environmental news to evergreen material. This also includes human interest stories, readings of eco-literature, discussion of film and other media productions of interest.
We are now living in the Age of Water. Water is the new “gold”, with individuals, corporations and countries positioning themselves around this precious resource. Water is changing everything. The Age of Water Podcast covers anything of interest from breaking environmental news to evergreen material. This also includes human interest stories, readings of eco-literature, discussion of film and other media productions of interest.


 Patricia Westerford—whose work resembles that of Diana Beresford-Kroeger (author of The Global Forest) and UBC’s
Patricia Westerford—whose work resembles that of Diana Beresford-Kroeger (author of The Global Forest) and UBC’s  In his review of Overstory in
In his review of Overstory in 
 Our predictions and visions of the future are certainly predicated on our perceptions of the present and the past. So, what happens when yesterday’s “future” collides with today’s past? Well, retro-fiction, alternate history and steam-punk, you quip, eyes askance with mischief: edgy sociopathic Sherlock Holmes with bipolar or obsessive /compulsive tendencies; flying aircraft carriers in Sky Captain and the World of Tomorrow, robot-like workers of Metropolis…
Our predictions and visions of the future are certainly predicated on our perceptions of the present and the past. So, what happens when yesterday’s “future” collides with today’s past? Well, retro-fiction, alternate history and steam-punk, you quip, eyes askance with mischief: edgy sociopathic Sherlock Holmes with bipolar or obsessive /compulsive tendencies; flying aircraft carriers in Sky Captain and the World of Tomorrow, robot-like workers of Metropolis…

 There are, in most cases, no technological impediments to the flying car, the jetpack, and moon-bases; only cultural ones. “These SF predictions ought to be viewed as visions of where we could be, as opposed to where we will be, or, keeping Bradbury in mind, visions of where we don’t want to go and, thankfully, have mostly managed to avoid to date,” says Steve Davidson of Grasping for the Wind. “Perhaps it’s all cultural,” he adds.
There are, in most cases, no technological impediments to the flying car, the jetpack, and moon-bases; only cultural ones. “These SF predictions ought to be viewed as visions of where we could be, as opposed to where we will be, or, keeping Bradbury in mind, visions of where we don’t want to go and, thankfully, have mostly managed to avoid to date,” says Steve Davidson of Grasping for the Wind. “Perhaps it’s all cultural,” he adds. George Orwell wrote his dystopian satire in 1949 about a mind-controlled society in response to the Cold War. The book was a metaphor “against totalitarianism and for democratic socialism,” said Orwell in his 1947 essay Why I Write, adding, “Good prose is like a windowpane.” Was Orwell’s Nineteen Eighty-Four a failed novel because the real 1984 didn’t turn out quite like his 1984? Hugo Award-winning novelist Robert J. Sawyer suggests that we consider it a success, “because it helped us avoid that future. So just be happy that the damn dirty apes haven’t taken over yet.”
George Orwell wrote his dystopian satire in 1949 about a mind-controlled society in response to the Cold War. The book was a metaphor “against totalitarianism and for democratic socialism,” said Orwell in his 1947 essay Why I Write, adding, “Good prose is like a windowpane.” Was Orwell’s Nineteen Eighty-Four a failed novel because the real 1984 didn’t turn out quite like his 1984? Hugo Award-winning novelist Robert J. Sawyer suggests that we consider it a success, “because it helped us avoid that future. So just be happy that the damn dirty apes haven’t taken over yet.” A hundred years before 1984, Edward Bellamy published Looking Backward, “a romance of an ideal world”. It tells the story of a young man who falls into a hypnotic sleep in 1887, waking up in 2000 when the world has evolved into a great socialist paradise. It sold over a million copies and ranked only behind Uncle Tom’s Cabin and Ben-Hur: A Tale of the Christ as the top best-seller of the era. Looking Backward laid out a futuristic socialism, or was it a socialistic future?
A hundred years before 1984, Edward Bellamy published Looking Backward, “a romance of an ideal world”. It tells the story of a young man who falls into a hypnotic sleep in 1887, waking up in 2000 when the world has evolved into a great socialist paradise. It sold over a million copies and ranked only behind Uncle Tom’s Cabin and Ben-Hur: A Tale of the Christ as the top best-seller of the era. Looking Backward laid out a futuristic socialism, or was it a socialistic future?
 In a foreward to a later printing of Brave New World years after it was first published, Aldous Huxley explained why, when given the chance to revise the later edition, he left it exactly as it was initially written twenty years earlier:
In a foreward to a later printing of Brave New World years after it was first published, Aldous Huxley explained why, when given the chance to revise the later edition, he left it exactly as it was initially written twenty years earlier:
 Proulx immerses the reader in rich sensory detail of a place and time, equally comfortable describing a white pine stand in Michigan and logging camp in Upper Gatineau to a Mi’kmaq village on the Nova Scotia coast or the stately Boston home of Charles Duquet. The foreshadowing of doom for the magnificent forests is cast by the shadow of how settlers treat the Mi’kmaq people. The fate of the forests and the Mi’kmaq are inextricably linked through settler disrespect and a fierce hunger for “more.”
Proulx immerses the reader in rich sensory detail of a place and time, equally comfortable describing a white pine stand in Michigan and logging camp in Upper Gatineau to a Mi’kmaq village on the Nova Scotia coast or the stately Boston home of Charles Duquet. The foreshadowing of doom for the magnificent forests is cast by the shadow of how settlers treat the Mi’kmaq people. The fate of the forests and the Mi’kmaq are inextricably linked through settler disrespect and a fierce hunger for “more.” “The reader comes to realize that the novel isn’t really about the human characters so much as it is about the forests,” Gus Powell of
“The reader comes to realize that the novel isn’t really about the human characters so much as it is about the forests,” Gus Powell of  In my recent novel
In my recent novel  The endocrine system is a set of glands and the hormones they produce that help guide and regulate the development, growth, reproduction and behavior of most living things (yes plants too!). Some hormones are also released from parts of the body that aren’t glands, like the stomach, intestines or nerve cells. These usually act closer to where they are released. The endocrine system is made up of glands, which secrete hormones, and receptor cells which detect and react to the hormones. Hormones travel throughout the body, acting as chemical messengers, and interact with cells that contain matching receptors. The hormone binds with the receptor, like a key into a lock. Some chemicals, both natural and human-made, may interfere with the hormonal system. They’re called endocrine disruptors.
The endocrine system is a set of glands and the hormones they produce that help guide and regulate the development, growth, reproduction and behavior of most living things (yes plants too!). Some hormones are also released from parts of the body that aren’t glands, like the stomach, intestines or nerve cells. These usually act closer to where they are released. The endocrine system is made up of glands, which secrete hormones, and receptor cells which detect and react to the hormones. Hormones travel throughout the body, acting as chemical messengers, and interact with cells that contain matching receptors. The hormone binds with the receptor, like a key into a lock. Some chemicals, both natural and human-made, may interfere with the hormonal system. They’re called endocrine disruptors.








 My short story “Out of the Silence,” which appeared in the Spring 2020 issue of
My short story “Out of the Silence,” which appeared in the Spring 2020 issue of 
 In her 1997 biography Rachel Carson: Witness for Nature, historian and science biographer Linda Lear wrote:
In her 1997 biography Rachel Carson: Witness for Nature, historian and science biographer Linda Lear wrote: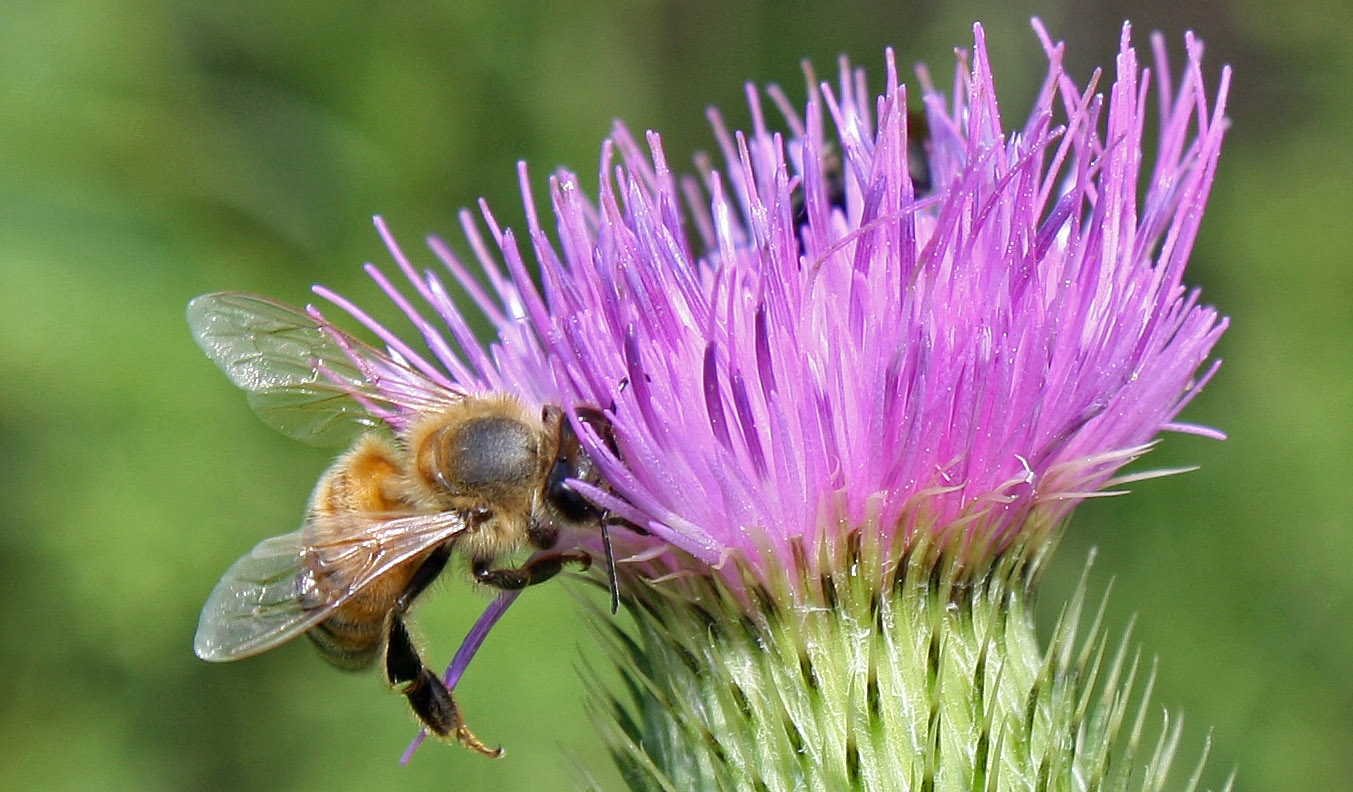
 “Miss Rachel Carson’s reference to the selfishness of insecticide manufacturers probably reflects her Communist sympathies, like a lot of our writers these days. We can live without birds and animals, but, as the current market slump shows, we cannot live without business. As for insects, isn’t it just like a woman to be scared to death of a few little bugs! As long as we have the H-bomb everything will be O.K.”
“Miss Rachel Carson’s reference to the selfishness of insecticide manufacturers probably reflects her Communist sympathies, like a lot of our writers these days. We can live without birds and animals, but, as the current market slump shows, we cannot live without business. As for insects, isn’t it just like a woman to be scared to death of a few little bugs! As long as we have the H-bomb everything will be O.K.”

