This past spring, Dutch scientist Herman van Dam (Consultancy for Water and Nature) approached me for permission to use my illustration of the diatom forest in a paper he and co-authors were preparing for the Dutch journal H2O. He explained that they wanted to help familiarize water managers who read the journal with the underwater biodiversity for which my illustration would be helpful.
The Illustration
He’d seen my illustration in my article “A Diatom Spring” in The Meaning of Water. Below is a summary of my article about the diatom forest:
Attachment and colonization starts with a ‘clean’ unpopulated surface (usually scoured by turbulence in a storm or some other event or a new surface tumbled into the water). Several stages of succession take place, starting with early colonizers. The adnate Cocconeis placentula, whose frustules attach directly to the substrate, is an example of an early colonizer. When they attach to a substrate they form a biofilm (think moss in a terrestrial forest). Adnate species are eventually overgrown by taxa that produce a mucilaginous pad (e.g. Synedra) or stalk (e.g. Gomphonema). The understory layer is typically occupied by diatoms such as Fragilaria vaucheriae and Synedra radians that attach to the surface at one end (apical) of their rod-shaped frustules using a mucilaginous pad to form “rosettes” that resemble spiky understory shrubs. This allows them to protrude above the adnate taxa and take advantage of more light.

The diatoms Cymbella and Gomphonema produce long stalks that attach directly to the surface, allowing them to form a swaying canopy over the lower tier of cells of Fragilaria vaucheriae, Synedra radians and early colonizer Cocconeis placentula whose frustules attach directly to the substrate (think overstory and understory of a terrestrial forest or a marine kelp forest).
The Diatom Forest Structure
Just like trees, the canopy-forming stalked diatoms effectively compete for available light and nutrients in the water with their vertical reach. They provide the ‘overstory’ of the diatom forest’s vertical stratification. These tree-like diatoms also provide an additional surface for other diatoms to colonize (e.g. tiny epiphytic Achnanthes settle on the long stalks of Cymbella, just as lichen does on a tree trunk).

The stalked diatom forest acts like a net, trapping drifting-in euplankton, such as Pediastrum sp. andFragilaria spp., which then decide to stay and settle in with the periphyton community. The mucilage captures and binds detrital particles in both lower and upper stories of the diatom forest; these, in turn, provide nutrients for the diatom forest and additional surfaces for colonization. In their work with periphyton communities, Roemer et al. (1984) found several diatoms (e.g. Diatoma vulgare, Fragilaria spp. Stephanodiscus minutula) entangled in the complex network of cells, stalks, and detritus of the diatom forest’s upper story. They also found rosettes of Synedra radians—like jungle orchids—attached to large clumps of sediment caught by the net of mucilage.
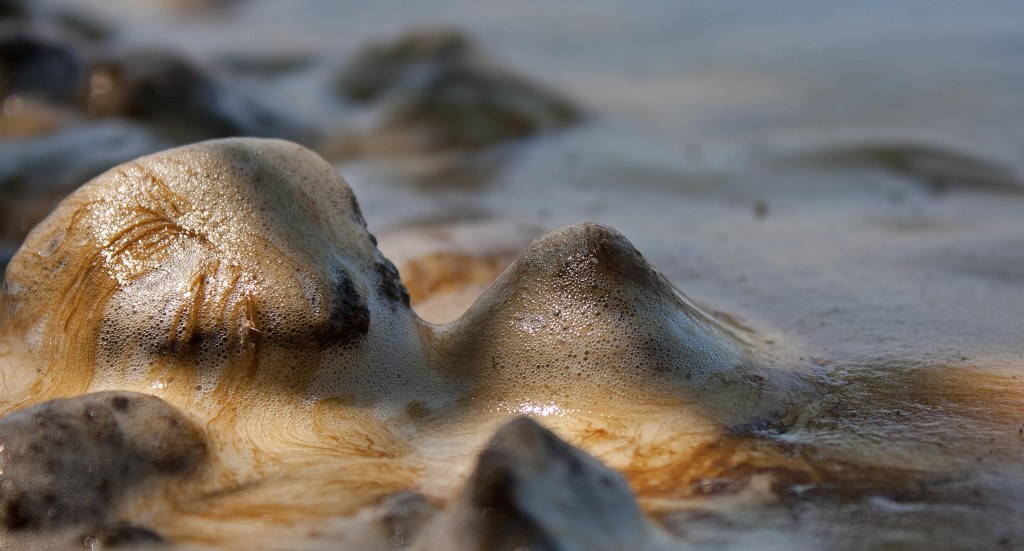
Eventually, ‘overgrowth’ occurs as the periphyton colony matures and grows ‘top-heavy’ with all this networking. The upper story of the community simply sloughs off—usually triggered by turbulence in a river from rains, storms, or dam release. This is similar to a forest fire in the Boreal forest, which creates space and light for new colonization and growth. The dislodged periphyton ride the turbulent flow, temporarily becoming plankton, and those that survive the crashing waters provide “seed” to colonize substrates downstream. Others may get damaged and form the ‘dish soap’ like suds or foam you often see in turbulent water. The proteins, lignins and lipids of the diatoms (and other associated algae) act as surfactants or foaming agents that trap air and form bubbles that stick to each other through surface tension.
The Paper

The paper was published June 13, 2024, in H2O, written by Jako van der Wal, Joep de Koning and Herman van Dam, and entitled “Snel inzicht in de ecologische waterkwaliteit met diatomeeën” (Quick insight into ecological water quality with diatoms). This paper was right up my alley! As a diatom specialist and limnologist who studied them in relation to environmental conditions and perturbations, I was intrigued by the paper and gained some additional insight on diatom ecology.
Van der Wal et al. cited recent advances in DNA-based identification methods that provide fast and cheap diatom identification over the traditional method of using an optical compound microscope to observe morphological characteristics such as size, shape and ornamentations of the silicified cell wall. I can attest that this is a labour-intensive process in which I spent many hours and days hunched over a microscope during my masters research at Concordia University. This efficient DNA-identification has seen a resurgence of using diatoms as a valuable tool for water quality managers, with applications providing insight into both current and historical water conditions. The authors argue that benthic diatoms or periphyton (living on substrates such as plants, rock, sand and artificial surfaces) have been since the 1980s used as indicators of saproby, trophy, acid and salt character in, among other things, ditches and canals. For every type of water and water quality, there are diatoms that have their habitat there, write the authors. They argue that, unlike phytoplankton, fish and macrofauna, periphyton attach to a surface and hardly move; this means that effects of water quality can be demonstrated locally. Because many diatom species tolerances and intolerances are known and they reproduce quickly (over days), diatoms respond quickly to changes in the environment—much faster (often within weeks) than other ecological indicators.
Scientists and water technicians can use diatom species composition to measure perturbations by organic material, low oxygen content, eutrophication, and toxicity. Given that diatoms colonize and develop quickly, this includes unstable and damaged habitats where other indicators cannot develop, such as shipping traffic, waves or where cleaning or dredging is carried out regularly. Historical insight can be provided by diatoms, given that their silica frustules are naturally preserved in sediment.
My Own Work with Turbulence
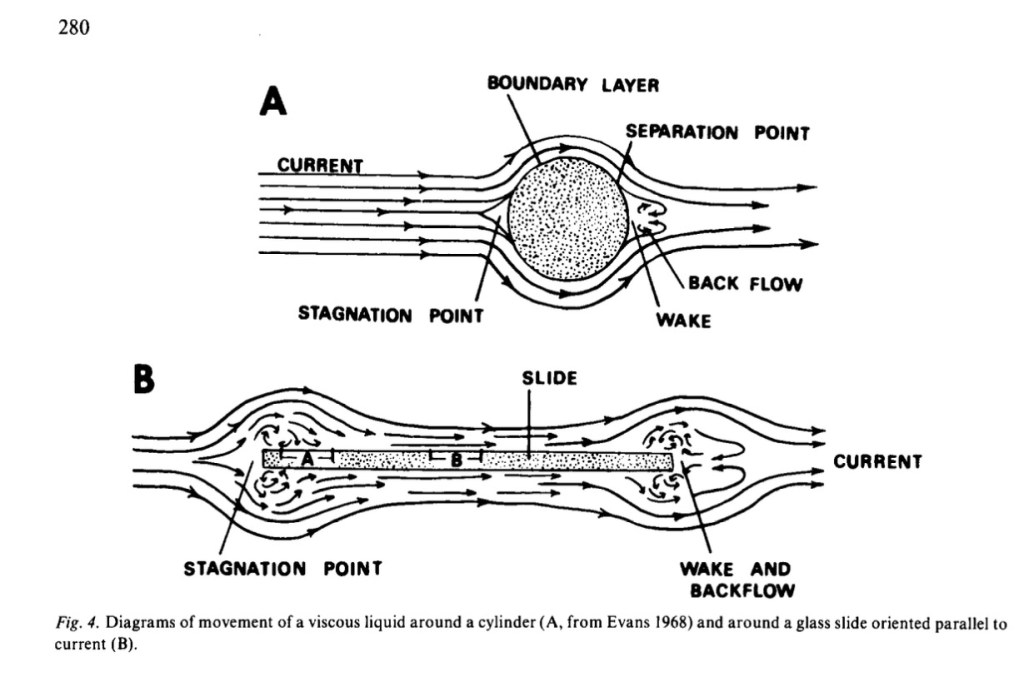
During my masters research in several streams in the Eastern Townships, I examined how diatoms colonized artificial substrates; how they formed productive biofilms that sustained an entire periphyton community of attached aquatic life and discovered that their pattern of colonization related to current speed and direction. I submerged glass slides (the kind people use to look at critters under the microscope) in a device in the stream and oriented them parallel or perpendicular to the current.
There are two ways an algal community grows in a new area: (1) by initial colonization and settling; and (2) by reproduction and growth. I studied both by collecting slides exposed for differing lengths of time (collecting young and mature communities) in different seasons.
I discovered that the diatoms colonized these surfaces in weird ways based on micro-turbulence. Early colonizers, like Achnanthes and adnate Cocconeis preferred to settle on the edges of the slides, where the chaos of turbulence ruled over the sheer of laminar flow. They colonized by directly appressing to the substrate, making them the first photosynthetic taxa to establish a biofilm on a clean substrate. Vadeboncoeur and Katona (2022) write that “in waved-washed surfaces, these taxa may be the only algae that persist.” I postulated that the drift velocity was reduced on the slide’s edge, where turbulence was greatest, giving drifting algae a greater chance to collide and settle on the slide over the more shear laminar flow along the slide’s central face.

Once settled, the community was more likely to grow with turbulence. Greater turbulence decreases the diffusion gradient of materials around algal cells, with a higher rate of nutrient uptake and respiration. Turbulence provides greater opportunity to an existing colony by increasing “chaotic” flow, potential collision and exchange. Turbulence is a kind of “stable chaos” that enhances vigor, robustness and communication.
Using Diatoms in Water Quality Assessments
In their paper Van der Wal et al. argued that in environmental assessment the DNA-identification is just one step in a process that looks a population structure and health. Diatoms are already used in 21 of the 27 EU countries as part of a Water Framework Directive (WFD) quality index for flowing waters and in nine EU countries for standing water. Example conditions and associated perturbations where diatoms are a particularly useful indicator include: salinity, acidity, oxygen saturation, organic load (saproby), nutrient richness (trophy), temperature, and toxicity.
Diatom Growth Forms & Deformities
Van der Wal et al. argued that in addition to the different species compositions and the related ecological indices, growth forms and deformations of diatoms are useful indicators of water quality, particularly in relation to specific toxins.
Growth forms of diatoms can be described as attached, short-stalked, long-stalked, mobile and living in mucous tubes (Figure 3, van der Wal et al., 2024). Each growth form has advantages and disadvantages. For example, short-stalked diatoms are more difficult to graze and long-stalked diatoms come into contact with more water, from which they can then absorb substances. Long-stalked diatoms can also absorb more light if there is a lot of competition. Mobile diatoms can adapt to changing conditions by, for example, migrating from surface to subsurface and vice versa. Diatoms in slime tubes are more difficult to prey on and respond more slowly to environmental changes.

According to Van der Wal et al., scientistis (Rimet & Bouchez) noted that long-stalked diatoms declined in waterbodies subjected to various pesticides. Falasco et al. observed diatom deformities when exposed to various toxic substances. Heavy metals were observed to cause deformities in Navicula. Nitrogen toxicity was also implicated in diatom deformities.
References:
Falasco, E., Ector, L., Wetzel, C.E., Badino, G. & Bona, F. (2021). “Looking back, looking forward: a review of the new literature on diatom teratological forms (2010-2020).” Hydrobiologia 848: 1675-1753.
Munteanu, N. 2022. “When Diatoms Create a Forest.” https://themeaningofwater.com. December 18, 2022.
Munteanu, N. 2023. “When Diatoms Bloom in Spring.” https://themeaningofwater.com. May 14, 2023.
Munteanu, N. 2023. “A Diatom Spring.” https://themeaningofwater.com. April 16, 2023.
Munteanu, N. & E. J. Maly, 1981. The effect of current on the distribution of diatoms settling on submerged glass slides. Hydrobiologia 78: 273–282.
Munteanu, Nina. 2016. “Water Is…The Meaning of Water.” Pixl Press, Delta, BC. 584 pp.
Poikane, S., Kelly, M., & Cantonati, M. (2016). ‘Benthic algal assessment of ecological status in European lakes and rivers: challenges and opportunities’. Science of the Total Environment 568: 603-613.
Rimet, F. & Bouchez, A. (2011). ‘Use of diatom life-forms and ecological guilds to assess pesticide contamination in rivers: Lotic mesocosm approaches’. Ecological Indicators 11: 489-499.
Roemer, Stephen C., Kyle D. Hoagland, and James R. Rosowski. 1984. “Development of a freshwater periphyton community as influenced by diatom mucilages.” Can. J. Bot. 62: 1799-1813.
Serôdio, J. & Lavaud, J. (2020). “Diatoms and their ecological importance”. In: Leal Filho, W. et al. (eds). Life below water. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (pp.1-9). Springer Nature.
Smolar-Zvanut, Natasa and Matjaz Mikos. “The impact of flow regulation by hydropower dams on the periphyton community in the Soca River, Slovenia. Hydrological Sciences Journal 59 (5): 1032-1045.
Wal, J. van der, Joep de Koning and Herman van Dam. 2024. “Snel inzicht in de ecologische waterkwaliteit met diatomeeën” H2O, 13 June, 2024.
Wood, Allison R. 2016. “Attached Algae as an Indicator of Water Quality: A Study of the Viability of Genomic Taxanomic Methods.” Honors Theses and Capstones. 306. University of New Hampshire Scholars’ Repository.
Zuilichem, H. van, Peeters, E. & Wal, J. van der (2016). “Diatomeeën als indicator voor waterkwaliteit nabij rwzi’s”. H2O-Online, 9 december 2016. https://edepot.wur.nl/401202

Nina Munteanu is a Canadian ecologist / limnologist and novelist. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” was published by Mincione Edizioni in Rome. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press(Vancouver) was selected by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times ‘Year in Reading’ and was chosen as the 2017 Summer Read by Water Canada. Her novel “A Diary in the Age of Water” was released by Inanna Publications (Toronto) in June 2020.