
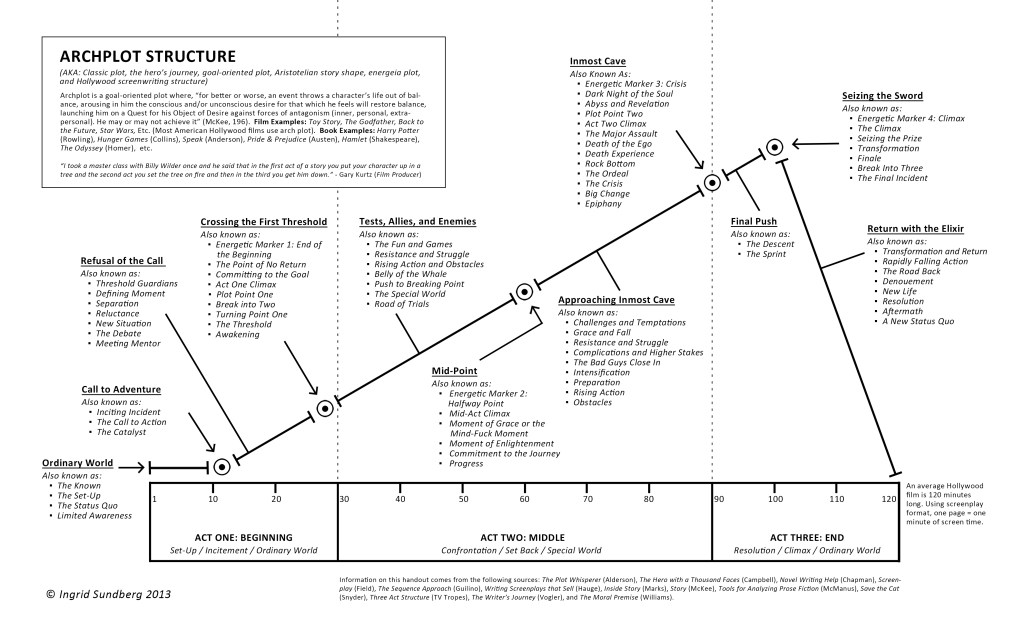
Rita Vrataski (Emily Blunt) fights a war against aliens
Some time ago on my birthday, I watched the popular — and somewhat controversial — Hunger Games. Well, controversial among some critics and followers of critics, anyway. I came across a particularly juicy article by critic Jeffrey Wells on Hollywood Elsewhere, in which he attributed the movie’s success to “reviews by certain female critics” who are “susceptible to the lore of this young-female-adult-propelled franchise.”
Whether this was true or not — and I highly doubt this — it brings up another stirring question: that of gender-bias. Is it truly still hard for a man like Wells to accept and enjoy a story which feature’s a female heroine? Is it so hard to see a woman as a person first: championing a cause, delivering a world from evil and injustice, overcoming a great obstacle to become enlightened?
I think of my favorite stories in literature, peopled by men and women; all heroes: Tess of the d’Urbervilles, Fahrenheit 451, King Lear, Solaris, The Grapes of Wrath, 1984, Doctor Zhivago, Brave New World, Martian Chronicles, and To Kill a Mockingbird — to name just a few. The gender of the hero I empathized with was irrelevant. What remained important was their sensibilities and their actions.

Katniss fights the system in Hunger Games
It got me thinking … What does it take to be a hero—a female hero— particularly? And does there need to be a difference? The tweets and FB-talk and Internet buzz imply that male heroes differ from female heroes; they embrace differing quests and archetypal roles and reflect different qualities. In his 2013 web-article “Saving Science Fiction From Strong Female Characters” SF author John C. Wright attempted to elucidate a more realistic portrayal of women heroes in science fiction. Unfortunately, the article relied heavily on well-established androcratic stereotypes.
The male hero stereotype in literature and films of western culture—and science fiction particularly—is often characterized by strength, courage, integrity & honor, intelligence, assertiveness, single-mindedness, faith in his quest, and boundless determination: he is the altruist warrior, often acting alone against an unfair society through his conscience. All traits honored, respected and esteemed in men. In a woman, these Boadicean qualities often qualify her as “a bitch” or a “tomboy”. She may be considered unwomanly, unlady-like, intimidating, and with lesbian tendencies. Not the sort of girl you would take home to Mummy. The exciting Becky Sharp to the prosaic but sweet Amelia. And God forbid that she is more intelligent than her male counterpart!

Kara Thrace (Starbuck) fights Cylons in Battlestar Galactica
For a woman to qualify as “hero” then, must she shed her feminine qualities of compassion, kindness, tenderness, and nurturing, to express those hero-defining qualities that are typically considered “male” to become less than either? Goddess untouchable? Women deserve better than that in literature and other story media. I have seen too many 2-dimensional female characters limited by their own stereotype in the science fiction genre—particularly in the adventure/thriller sub-genre. If they aren’t untouchable goddesses or “witches” in a gynocratic paradigm (woman-dominating), they are often delegated to the role of enabling the “real hero” on his journey through their belief in him: as Trinity enables Neo; Hermione enables Harry; Mary Jane enables Spiderman; Lois enables Superman; etc. etc. etc.

Aeryn Sun (Claudia Black) fights “humans” in Farscape
In an opinion piece in The Detroit News, Tom Long tells us that the women in top hero-style movies have usually been and still are portrayed in “romantic, sidekick or comedic roles. Often they’re waiting to be rescued (think Princess Leia). And some of them are part of action ensembles [think X-men].” Token figures to provide added “spice”, edge and diversity. This is, according to Gitesh Pandya, editor of a box office analyst site, because female-driven action movies have a hard time selling. “Most of the action films that have become huge hits are either male-driven or ensemble.” Pandya goes on to suggest that this is because more tickets are purchased by men than by women. “The film industry has been male-dominated for so long, the people who are creating and financing these films typically put men in there as heroes.” And yet women read far more fiction than men (by a 4:1 ratio according to some sources). We are in dire need of balance and we hunger for a female hero.

Lucy: victim, predator or neither?
“What does it mean for our nation or our world if we treat [women] by a different script? What are we clinging to when we cling to that script that women need men’s protection?” said Ann Folino White, assistant professor at Michigan State University. She does well to call it a script when the storytellers of a culture define our humanity: who and what we are, our values and what we strive to be. Storytellers are the shamans of our culture and our time. We are the visionaries of our future.
The recent SF action film Edge of Tomorrow provided a refreshing kind of woman hero; Rita Vrataski (Emily Blunt) is equal—in fact superior—to her male protagonist, William Cage (played by Tom Cruise) in skill, intelligence and heroic stature. What I mean by heroic stature is that her heroic journey of transformation does not play subservient to her male counterpart’s journey.
 In so many androcratic storylines, the female—no matter how complex, interesting and tough she starts out being—must demure to the male lead; as if only by bowing down to his superior abilities can she help ensure his heroic stature. Returning us right back to the cliché role of the woman supporting the leading man to complete his hero’s journey. And this often means serving as the prize for his chivalry. We see this in so many action thrillers and action adventures today: Valka in How to Train Your Dragon, Wyldstyle in The Lego Movie, Neytiri in Avatar, Trinity in The Matrix, and so many more. There’s even a name for it: the Trinity Syndrome.
In so many androcratic storylines, the female—no matter how complex, interesting and tough she starts out being—must demure to the male lead; as if only by bowing down to his superior abilities can she help ensure his heroic stature. Returning us right back to the cliché role of the woman supporting the leading man to complete his hero’s journey. And this often means serving as the prize for his chivalry. We see this in so many action thrillers and action adventures today: Valka in How to Train Your Dragon, Wyldstyle in The Lego Movie, Neytiri in Avatar, Trinity in The Matrix, and so many more. There’s even a name for it: the Trinity Syndrome.
Tasha Robinson writes in her excellent article entitled, We’re losing all our Strong Female Characters to Trinity Syndrome: “The idea of the Strong Female Character—someone with her own identity, agenda, and story purpose—has thoroughly pervaded the conversation about what’s wrong with the way women are often perceived and portrayed today, in comics, video-games, and film especially…it’s still rare to see films in the mainstream action/horror/science-fiction/fantasy realm introduce women with any kind of meaningful strength, or women who go past a few simple stereotypes.”

Rita Vrataski poster girl for the war
I give Edge of Tomorrow full marks for not doing this. For example, after Cage makes his case to his Squadron to go on a mission, they remain reluctant until Vrataski emerges. “I don’t expect you to follow me,” says Cage. “I do expect you to follow her.” The Angel of Verdun—or better yet, the badass Full Metal Bitch.
When a female lead is stronger than the male protagonist, some reviewers (OK—male reviewers) categorize that movie as a “woman’s story”. I’ve been told by some of my male friends that they couldn’t possibly empathize with such a character—mainly because she is a woman and she is stronger than the male lead that “they want to be”. It would appear that men are less willing to empathize with a woman character than a woman is willing to empathize with a male character; something in itself interesting. Invariably, in many of these “goddess” stories, the male counterpart is so much “milk-toast” compared to that awesome female-warrior. And have you ever noticed that, while the male hero gets the girl, the female hero usually ends up alone? Great examples include: Buffy the Vampire Slayer; Xena: Warrior Princess; Sarah in The Terminator and of course Vasquez in Aliens. These women are amazons; they stand apart, goddess-like, unrelenting, unflinching—untouchable. It’s actually no wonder that my ex-husband dislikes Sigourney Weaver to this day—she could crush him underfoot and eat him for breakfast at a moment’s notice. And probably would!
In a superb article in NewStatesman entitled I hate Strong Female Characters, Sophia McDougall says:
“…I want to point out two things that Richard II has, that Bond and Captain America and Batman also have, that Peggy (Carter of Captain America), however strong she is, cannot attain. They are very simple things, even more fundamental than “agency”
-
Richard has the spotlight. However weak or distressed or passive he may be, he’s the main goddamn character
-
Richard has a huge range of other characters of his own gender around him, so that he never has to act as any kind of ambassador or representative for maleness. Even dethroned and imprisoned, he is free to be uniquely himself. On the posters [women are] posed way in the back of the shot behind the men, in the trailers they may pout or smile or kick things, but they remain silent. Their strength lets them, briefly, dominate bystanders but never dominate the plot. It’s an anodyne, a sop, a Trojan Horse – it’s there to distract and confuse you, so you forget to ask for more.”
There is another type of female hero. She is equal to her male counterpart. Her story is not secondary to his story; her heroic status and hero’s journey is equal to his and not because he’s been reduced to a lesser character, diminished by her or overshadowed by her; in fact they may share the same journey. Examples include: Bonnie and Clyde; Peter Chang’s Aeon Flux; Aeryn Sun and John Crichton in Farscape; Starbuck and Apollo in Battlestar Galactica…And now Vrataski and Cage in Edge of Tomorrow.

Cage and Vrataski discuss strategy
As with the above examples, Vrataski and Cage in Edge of Tomorrow form a team, in which together they are more than the sum of their parts. A marriage of independent autopoiesis, combining skills, abilities and vision. This is also why, in my opinion, the ending of Edge of Tomorrow is totally appropriate: not because it’s “the happy ending”; but because it carries the message of enduring collaboration of equals in a gylanic society.
So, in the end, I do agree with John C. Wright that science fiction requires whole female characters, but not for the reasons he gives.
The gylanic hero is emerging in science fiction and action-thrillers, one who will teach us more about what humanity needs now more than ever: the heroic gifts of altruism, compassion, faith, courage, passion, and endurance. She is already there, in movies and TV shows like Lucy, Edge of Tomorrow, Hunger Games, Divergence, Orphan Black, Farscape, Battlestar Galactica: fighting the dragons of prejudice, ignorance, cruelty, greed and intolerance–in partnership with her male counterpart.

Aeryn Sun and John Crichton collaborate in Farscape
A list of SF books with whole and relevant female heroes–gylanic heroes– follows below. There are many more. I’ve listed these because they are ones I enjoyed and know, several being my own. Please add yours:
GYLANIC HEROES
- The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins (Scholastic Press). 2008. A series of books about teens forced to fight to the death on television.
- The Steel Seraglio by Mike Carey, Linda Carey, Louise Carey and Nimit Malavia (Chizine Publications). 2012. A novel about the women of a harem in an ancient Middle Eastern kingdom, who forge themselves into an army after they’re exiled from the city of their birth — and then return to claim the city for themselves.
 The Splintered Universe Trilogy by Nina Munteanu (Starfire). 2011-2014. This trilogy, starting with Outer Diverse, follows the quest of Galactic Guardian Rhea Hawke, a wounded hero who must solve the massacre of a spiritual sect that takes her on her own metaphoric journey of self-discovery to realize power in compassion and forgiveness.
The Splintered Universe Trilogy by Nina Munteanu (Starfire). 2011-2014. This trilogy, starting with Outer Diverse, follows the quest of Galactic Guardian Rhea Hawke, a wounded hero who must solve the massacre of a spiritual sect that takes her on her own metaphoric journey of self-discovery to realize power in compassion and forgiveness.
- Divergent by Veronica Roth (Katherine Tegen Books) 2012. a young girl overcomes her assigned caste in a dystopian Chicago to realize her true self-identity, revealed to be dangerous to the very existence of her ordered society
- Cordelia’s Honor by Lois McMaster Bujold (Baen). 1999. A woman’s journey through deception and betrayal to find honour.
- Contact by Carl Sagan (Simon and Schuster) 1985. A woman’s quest into the unknown for benevolent intelligence in the universe.
 Darwin’s Paradox by Nina Munteanu (Dragon Moon Press). 2007. An eco-thriller about a woman unjustly exiled for murder and her quest for justice in a world ruled by technology and scientists.
Darwin’s Paradox by Nina Munteanu (Dragon Moon Press). 2007. An eco-thriller about a woman unjustly exiled for murder and her quest for justice in a world ruled by technology and scientists.
- Beggars in Spain by Nancy Kress (Harper Collins). 1993. A story that examines social consequences to transhumanist generic engineering.
- His Dark Materials Trilogy by Philip Pullman (Laurel Leaf). 2003. A fantasy alternate world adventure about a young girl who discovers that the fate of the universe lies in her hands.
- A Handmaid’s Tale by Margaret Atwood (Anchor). 1998. A chilling fable of the near future, about a monotheocratic government where women are strictly controlled and assigned roles.
 The Last Summoner by Nina Munteanu (Starfire). 2012. A young baroness discovers that her strange powers enable her to change history … but at a cost. Vivianne begins her journey in the year 1410, on the eve of a great battle. She dreams of her Ritter (knight), who will save her from her ill-fated marriage and the strange events that follow. But early on, she realizes that she is the Ritter she keeps dreaming about. She must save herself and her world.
The Last Summoner by Nina Munteanu (Starfire). 2012. A young baroness discovers that her strange powers enable her to change history … but at a cost. Vivianne begins her journey in the year 1410, on the eve of a great battle. She dreams of her Ritter (knight), who will save her from her ill-fated marriage and the strange events that follow. But early on, she realizes that she is the Ritter she keeps dreaming about. She must save herself and her world.
Other Relevant Articles of Interest from The Alien Next Door:
Gylany: a social system based on equality of men and women
Androcracy: a form of governing system in which rulers are male
Riane Eisler (in The Chalice and the Blade) provides examples of sociobiologists who draw on nineteenth-century Darwinism by citing  insect societies to support their androcratic (social and political rule by men) theories. If humanity is to truly rise victorious over the scourge of climate change—a function of our current lifestyle and paradigms—we will need to adopt a cultural evolution that embraces a partnership society heralded by new and renewed symbology, language and “myth”: It starts with embracing gylanic heroes in literature and movies. Watching them, reading about them, writing and sharing these stories for the future they speak to.
insect societies to support their androcratic (social and political rule by men) theories. If humanity is to truly rise victorious over the scourge of climate change—a function of our current lifestyle and paradigms—we will need to adopt a cultural evolution that embraces a partnership society heralded by new and renewed symbology, language and “myth”: It starts with embracing gylanic heroes in literature and movies. Watching them, reading about them, writing and sharing these stories for the future they speak to.
 Nina Munteanu is an ecologist and internationally published author of award-nominated speculative novels, short stories and non-fiction. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books.
Nina Munteanu is an ecologist and internationally published author of award-nominated speculative novels, short stories and non-fiction. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books.



















 The Splintered Universe Trilogy by Nina Munteanu (Starfire). 2011-2014. This trilogy, starting with Outer Diverse, follows the quest of Galactic Guardian Rhea Hawke, a wounded hero who must solve the massacre of a spiritual sect that takes her on her own metaphoric journey of self-discovery to realize power in compassion and forgiveness.
The Splintered Universe Trilogy by Nina Munteanu (Starfire). 2011-2014. This trilogy, starting with Outer Diverse, follows the quest of Galactic Guardian Rhea Hawke, a wounded hero who must solve the massacre of a spiritual sect that takes her on her own metaphoric journey of self-discovery to realize power in compassion and forgiveness. Darwin’s Paradox by Nina Munteanu (Dragon Moon Press). 2007. An eco-thriller about a woman unjustly exiled for murder and her quest for justice in a world ruled by technology and scientists.
Darwin’s Paradox by Nina Munteanu (Dragon Moon Press). 2007. An eco-thriller about a woman unjustly exiled for murder and her quest for justice in a world ruled by technology and scientists. The Last Summoner by Nina Munteanu (Starfire). 2012. A young baroness discovers that her strange powers enable her to change history … but at a cost. Vivianne begins her journey in the year 1410, on the eve of a great battle. She dreams of her Ritter (knight), who will save her from her ill-fated marriage and the strange events that follow. But early on, she realizes that she is the Ritter she keeps dreaming about. She must save herself and her world.
The Last Summoner by Nina Munteanu (Starfire). 2012. A young baroness discovers that her strange powers enable her to change history … but at a cost. Vivianne begins her journey in the year 1410, on the eve of a great battle. She dreams of her Ritter (knight), who will save her from her ill-fated marriage and the strange events that follow. But early on, she realizes that she is the Ritter she keeps dreaming about. She must save herself and her world.






