Shimmering Water by Lawren Harris
2020 marks the centenary of the formation of the Canadian iconic Group of Seven artists. The Group of Seven movement “dragged Canadian art into the modern age,” writes Christine Sismondo of The Toronto Star in her review of “The Group of Seven Reimagined,” an ekphrastic celebration of the Group of Seven by twenty-one flash fiction authors (including my own “Alien Landscape” inspired by J.E.H. MacDonald’s Lake O’Hara). Sismondo astutely identifies and encapsulates the resonant meaning of the Group of Seven, then and now:
“A hundred years ago, seven Canadian painters got together and decided to start a movement. It was born out of the horrors of war. Now, the potential horrors of climate change are giving the movement an unexpected new life and meaning.”

Jack Pine by Tom Thomson
Sismondo goes on to describe how the movement itself took form:
“At the time, people were trying to put the horrors and sacrifices of the Great War behind them and look to the future to reimagine and redefine Canada itself. It was a pivotal moment, given the role the country had recently played in international affairs and the challenges it faced in becoming an increasingly modern nation. These seven artists—friends and colleagues, many of whom worked together in a Toronto design firm—felt they could help shape this conversation with bold strokes and bright colours to bring out the beauty of the Canadian landscape.”
But in those early days—and more than thirty years after Van Gogh painted Starry Night, Canada still wasn’t ready for Impressionism, or any other art form whose roots came from that movement. Canadian critics disliked the Group of Seven. They were too modern, too experimental. The Group were dismissed as “the Hot Mush School” “a horrible bunch of junk” “the figments of a drunkard’s dream” and “daubing by immature children.”

Mirror Lake by Franklin Carmichael
In his article on the Group of Seven’s reception in England vs Canada, Adam Bunch writes about the reception of the Group of Seven shortly after their formation after the First World War:

The Entrance to Halifax Harbour by A.Y. Jackson
“The reviews by Canadian critics were harsh. The Toronto Daily Star compared Jackson’s work to “a spilt can of paint.” But the English critics loved it. The Morning Post called the Group of Seven “the foundation of what may become one of the greatest schools of landscape painting.” One piece of Canadian art was even sold during the British Empire Exhibition — and it was Jackson’s. Entrance To Halifax Harbour was bought by the Tate Gallery. It’s still part of their collection today.”
“And despite the poor Canadian reviews, the show in London helped to establish the Group of Seven’s reputation back home. Now that the British took the Group seriously, Canadian collectors started taking them seriously, too. The Group even used the bad press to promote their upcoming shows: they printed posters with the angry Canadian reviews side by side with the glowing English ones.”

The Group of Seven Reimagined, published by Heritage House, was elegantly edited by flash fiction author Karen Schauber. Karen had invited me to contribute a piece of flash fiction (a piece of less than 500 words), inspired by a Group of Seven piece I would chose to inspire me. I took my time; this would be the first flash fiction piece I would write. It was an art form I was not familiar with, but was happy to experiment with. But I waited too long to decide and when I finally submitted my first choice for a painting, Karen informed me that it had already been selected by another writer. To my great frustration, this went on for a few pieces.

Shore Pattern by A.J. Casson
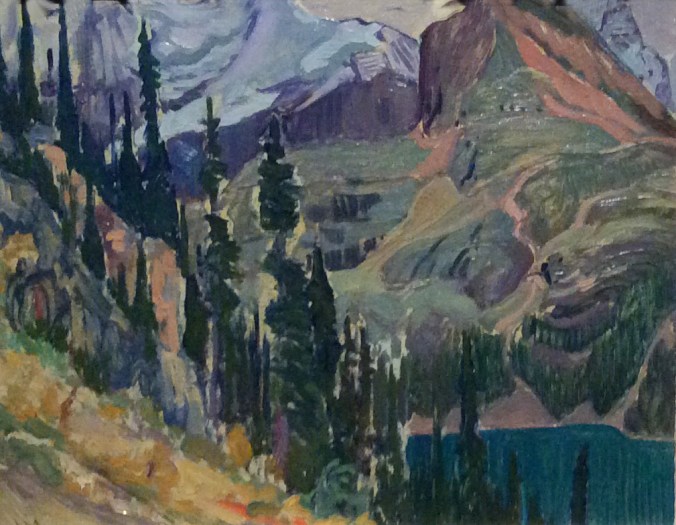
I finally took a short trip to the McMichael Gallery in Kleinburg to find my piece. In the main hall, I passed the pieces already claimed by my twenty colleagues; I sighed that I had waited so long. By chance, a large selection of artwork by J.E.H. MacDonald—one of the founders of the group—was currently on exhibit on the second floor. That was where I first saw the original oil sketch called Lake O’Hara by MacDonald. It was perfect! My story “Alien Landscape” emerged from the sketch like they had always belonged together.

Lake O’Hara by JEH MacDonald
The Star wrote: “while you might expect a lot of peaceful communing with nature on the page, a surprising number of the written pieces are actually dark tales of conflict and danger—forest fires, mining accidents, boat thieves and murderous plots in the woods. Nina Munteanu, a Canadian ecologist and science-fiction writer, takes J.E.H. MacDonald’s Lake O’Hara in a novel direction in ‘Alien Landscape’ by reimagining it as a refuge for a space heroine fleeing a world that had destroyed nature in pursuit of progress and ended in post-apocalyptic chaos.”

Gift shop at McMichael Gallery
The anthology has found itself gracing the gift shop shelves of several art galleries and museums such as the Royal BC Museum in Victoria, BC, and the McMichael Gallery in Kleinburg. It has likewise received much praise and accolades and appears on several ‘best of’ lists for ekphrastic works, art books, and more.
The anthology was long-listed for The Miramichi Reader’s “The Very Best” Book Award for 2020. The Miramichi Reader writes:

Sunset in the Bush by Frank Johnston
“There’s a very good reason that as I write this, The Group of Seven Reimagined, Contemporary Stories Inspired by Historic Canadian Paintings is sitting at, or near the top of bestseller lists in Canada (currently #3 on the Canadian Art bestseller list at Amazon.ca). The result is a most attractive book that any lover of art and literature would enjoy, even if they already have more than a passing familiarity with the iconic Group of Seven. All the stories that accompany each image are in the “flash fiction” style, just a page or two in length, a little story that the authors were inspired to write after choosing a particular G7 painting.”
Jules Torti of Cottage Life describd the book this way:
“Seeking equilibrium? This book is like a yoga session without the scheduling logistics and hustle to class. Balance is found in The Group of Seven Reimagined both as an intelligent coffee table book and tangible source of meditation.

Authors of the anthology
Twenty-five writers with notable street cred contributed “flash fiction” to colour iconic paintings by the Group of Seven (and their tagalongs). Flash fiction are stories categorized by length—they are 500 words or less which means they allow for one decent, undistracted cup of dark roast or whisky on ice. For writers or artists, the temptation to reimagine these works will be irresistible. And, what an intriguing resolution to make! Fiction and paintings both rely on interpretation and consideration. Fill in the gaps and colours with your chosen or perhaps newly discovered medium (watercolour?). As Jim and Sue Waddington suggest in the foreword, an art gallery visit becomes suspended in time. We keep returning to certain paintings that resonate and haunt and inadvertently, ‘Your mind sets off on a journey.’”
Author and reviewer Patricia Sandberg describes the anthology through metaphor: “Like a fine wine with dinner, some things cry out to be paired. In Reimagined, the nearly hundred-year-old brandy that was the Group of Seven is introduced to a fresh vibrant cuisine that is flash fiction, and both are the richer for it.”

Stormy Weather by Frederick H. Varley
“As a disciple of the Group of Seven and an aficionado of Canadian wilderness, every page gives me a little leap of pleasure.”—Robert Bateman
“These sharp, imaginative evocations of the world of the Group of Seven are both a joy in themselves and a welcome prompt to make us look at the paintings again. It’s refreshing to find that, a century later, they still speak to us about our lives and our country.”—Ross King, author of Defiant Spirits: The Modernist Revolution of the Group of Seven

Nina Munteanu with the anthology
“Words, the writer’s paint, are artfully chosen and applied, not one wasted. The stories all compel the reader to dive beneath their surface and linger long after the reading is complete…In 1920 The Group of Seven introduced a new vision for the Canadian landscape. One hundred years later, twenty-one writers in the Group of Seven Reimagined offer a new lens for appreciating their art.”—Ottawa Review of Books
“From one region of Canada to another, a national identity is captured and shared with writers all over the world who, in turn, have crafted beautiful flash fiction pieces that accompany and extend the meaning of the art.”—Niles Reddick, Literary Heist

Nina Munteanu is a Canadian ecologist / limnologist and novelist. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” was published by Mincione Edizioni in Rome. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press (Vancouver) was selected by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times ‘Year in Reading’ and was chosen as the 2017 Summer Read by Water Canada. Her novel “A Diary in the Age of Water” will be released by Inanna Publications (Toronto) in May 2020.