.
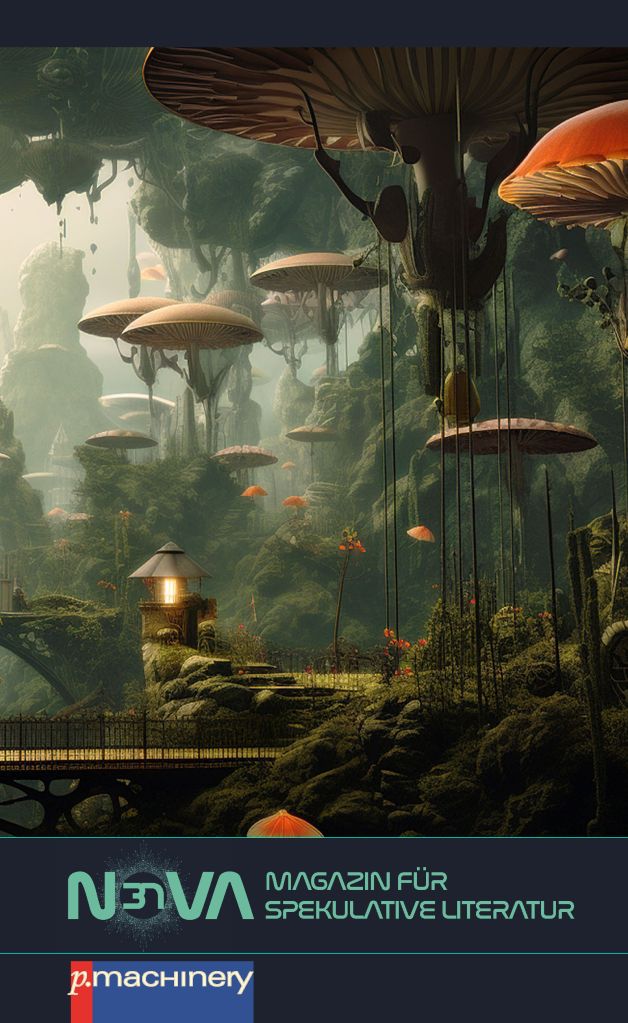
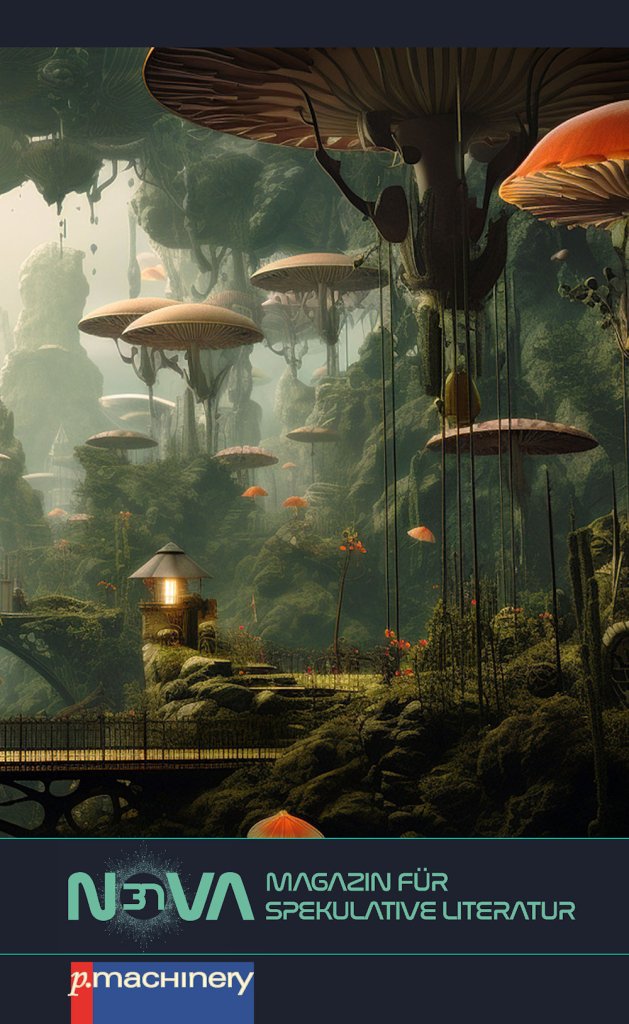
My short story “The Way of Water” was recently translated into German (“Der Weg des Wassers”) and published in Nova 37. The issue has illustrations for each story and a beautiful cover. When I got my author’s copy in the mail, I was blown away! It was as though they had tapped my love for mushrooms. Bright orange and floating in a sea of green vegetation, the aerial fungi that hovered over a jungle village resembled giant Micenas.
“The Way of Water” follows a young woman (Hilda) in near-future Toronto who has run out of water credits for the public iTap; by this time houses no longer have potable water and their water taps have been cemented shut (as was done in Detroit in 2014); the only way to get water is through the public iTaps—at great cost. She’s standing two metres from water—in a line of people waiting to use the tap—and dying of thirst.
“The Way of Water” captures a vision that explores the nuances of corporate and government corruption and deceit together with global resource warfare. In this near-future, Canada is mined of all its water by thirsty Chinese and US multinationals—leaving nothing for the Canadians. Rain has not fallen on Canadian soil in years due to advances in geoengineering and weather manipulation that prevent rain clouds from going anywhere north of the Canada-US border. If you’re wondering if this is possible, it’s already happening in China and surrounding countries.
I’ve written several articles on how The Way of Water came about. Briefly, it all started with an invitation in 2015 by my publisher in Rome to write about water and politics in Canada. I had long been thinking of potential ironies in Canada’s water-rich heritage. The premise I wanted to explore was the irony of people in a water-rich nation experiencing water scarcity: living under a government-imposed daily water quota of 5 litres as water bottling and utility companies took it all.
.
.
The Way of Water was first published in 2016 as a bilingual print book by Mincione Edizioni (Rome) in Italian (La natura dell’acqua, translated by Fiorella Moscatello), and English along with a recounting of what inspired it: The Story of Water (La storia dell’acqua). To date, The Way of Water has been published and republished eight times throughout the world and translated into Italian and German. Anthologies include, among others, Metastellar something, “Canadian Tales of Climate Change” (Exile Editions) edited by Bruce Meyer, “Future Fiction” Anthology (publisher), and “Climate in Crisis” (Little Blue Marble). I think this success is less a reflection of my writing than the immediacy and importance of the topic covered: growing water scarcity, its commodification, and its politicization.
.
This latest publication of The Way of Water (Der Weg des Wassers) in Nova 37 represents its eighth publication. Nova Magazin für spekulative Literatur is one of the most respected short story and essay magazines for science fiction in the German-speaking world. Most recently it was called “NOVA Science-Fiction,” and since issue 31 it has been “NOVA – Magazine for Speculative Literature”; the name change reflects the desire to broaden the readership and interest beyond the pure science fiction scene. The magazine’s website is now part of the larger pmachinery.de news feed.

.
“In a short story in which every word has its weight, Nina Munteanu manages to describe a dystopia with ecological, political, social and economic elements and Hilda’s reactions to her situation with a great intensity. To avoid thirst, Hilda ends up embracing an extreme idea, a last hope linked to water. The Way of Water is a story of the kind you hope is science fiction but you fear is not.”—Massimo Luciani
“In the Way to Water, Nina Munteanu pens her love letter to water, exulting it as a liquid that has semi-magical properties… The Way of Water evokes a sense of awareness about issues of access to water and about the dangers of imbalances in that access.”—Derek Newman-Stille, Speculating Canada
.
.
In her masters thesis published in November 2025 at the University of Graz, Austria, Seyma Yonar uses my short story The Way of Water, along with several others to explore and discuss the importance of eco-literature in establishing ecological awareness and ultimately ecological and sustainable action.
“The Way of Water is a strong eco-story that possesses many layers and elements that strengthen its narrative while encouraging readers to engage with its world…The notion what water constitutes the essence of life is the central theme of the story … Munteanu’s knowledge as a scientist enables her to create a convincing scientist protagonist whom she embeds into a powerful fictional story. Water, particularly in this eco-story acts not only as a symbolic entity but also as a body of force…the agency of water is presented as a dynamic, living entity, central to the narrative’s ecological themes.”
“Munteanu’s impactful storytelling highlights her significant contribution to Canadian literature, particularly through her engagement with pressing environmental issues and her commitment to fostering ecological awareness through fiction.”
.
.
The Way of Water, in turn, inspired my dystopian novel A Diary in the Age of Water (Inanna Publications, 2020), which chronicles the lives of four generations of women and their relationship to water during a time of severe water restriction and calamitous climate change. The novel features the main character Hilda from The Way of Water and her limnologist mother; A Diary in the Age of Water is essentially the mother’s diary embedded in a larger story. Through a series of entries, the diarist reflects on the subtle though catastrophic occurrences that will eventually lead to humanity’s demise.
.
.
References:
Munteanu, Nina. “The Way of Water” Mincione Edizioni, Rome. 113pp.
Munteanu, Nina. “A Diary in the Age of Water.” Inanna Publications, Toronto, ON. 328pp.
Meyer, Bruce. 2017. “Introduction to “Cli Fi: Canadian Tales of Climate Change“
Fi: Anthology #14. Edited by Bruce Meyer. Exile Editions, Toronto.304pp.
Yonar, Seyma. 2025. “Short Texts—Long Term Effects: The Canadian Eco-Story.” Masters Thesis, University of Graz, Austria. 70pp.
.
.

Nina Munteanu is an award-winning novelist and short story writer of eco-fiction, science fiction and fantasy. She also has three writing guides out: The Fiction Writer; The Journal Writer; and The Ecology of Writing and teaches fiction writing and technical writing at university and online. Check the Publications page on this site for a summary of what she has out there. Nina teaches writing at the University of Toronto and has been coaching fiction and non-fiction authors for over 20 years. You can find Nina’s short podcasts on writing on YouTube. Check out this site for more author advice from how to write a synopsis to finding your muse and the art and science of writing. For more on her work as a limnologist and ecologist, see The Meaning of Water.
.