.
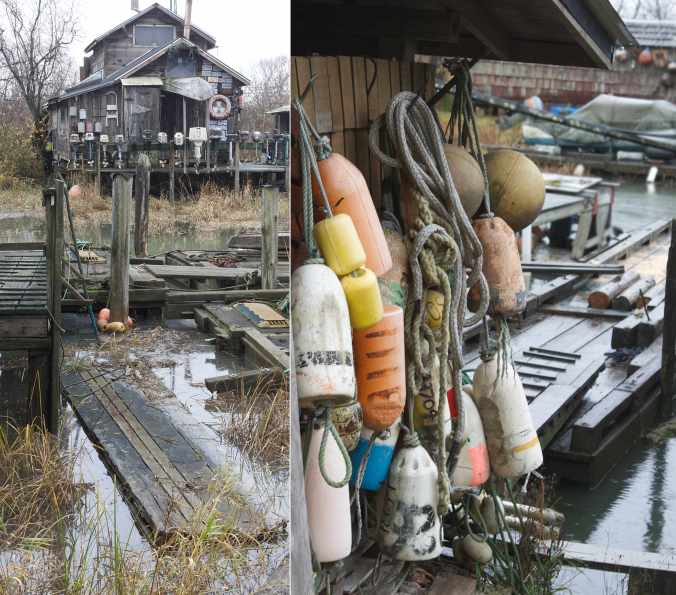
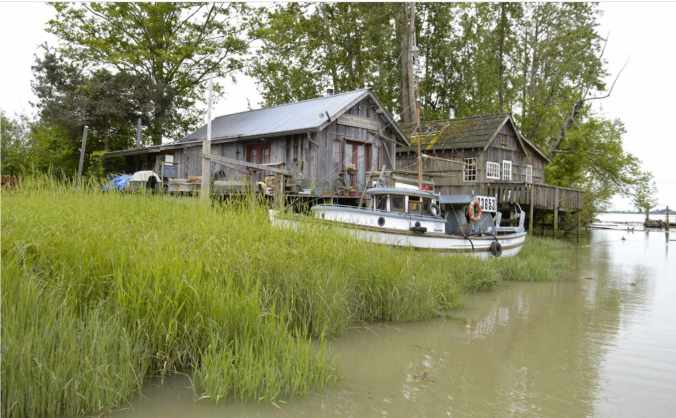
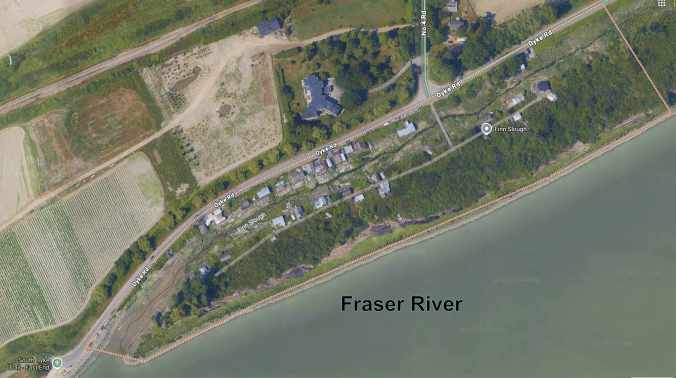
Not long ago, I went for a drive through the pastoral area of Lulu Island and ended up heading south along No. 4 Road in Steveston. As I wound my way toward Dyke Road, I found myself revisiting an old haunt from years ago: the little homesteader community—former Finnish fishing village—of Finn Slough. I remember first discovering this rather charming and eclectic settlement perched on stilted houses along the marsh of Finn Slough back in the 1980s when I briefly lived in Richmond. A sign by the bridge across the slough to Gilmour Island, where Number 4 Road meets Dyke Rd, provides a history of the Finnish community by Historian and Archivist David Dorrington who describes Finn Slough as a place “where nature and history gently coexist.”
.
.
The area was settled in the late 1880s by immigrant Finnish fishermen and their families, seeking a new life from the poverty and repression of the Russian empire in Finland. They built their buildings on pilings to accommodate the changing tides. One of the first and most important buildings was a sauna. The fishing community also built bluestone tanks, used to clean their linen nets. They also had rack floats and net sheds. In those days—when downtown Richmond didn’t exist—it would take an entire day to go one way from Finn Slough to Vancouver (now a 30-minute drive). Steveston was pretty much only canneries. Once a week, says the sign, the Finnish community would dress up in their ‘best clothes’ and take several boats to Steveston, Ladner or New Westminster to buy the week’s supplies. And if the weather was good, they would have a picnic on one of the river islands and sing along with accordion music. The homesteader village established without property boundaries, city ordinances, provincial regulations or any governing body.
.
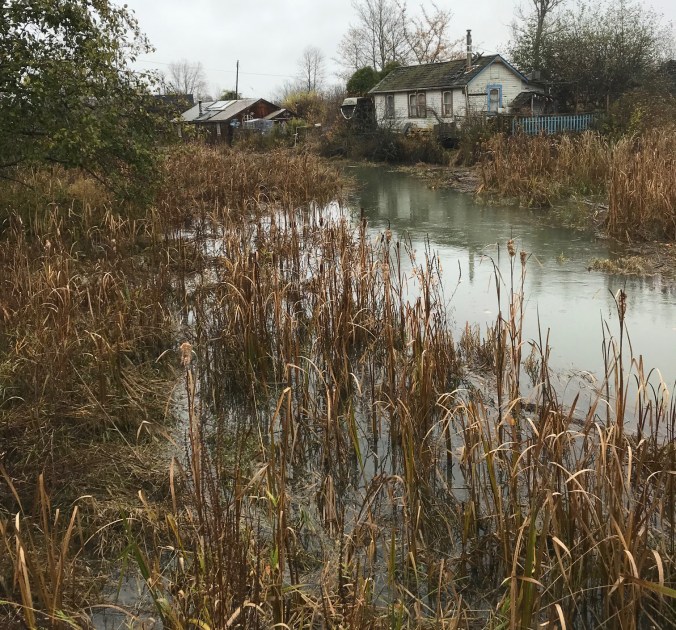

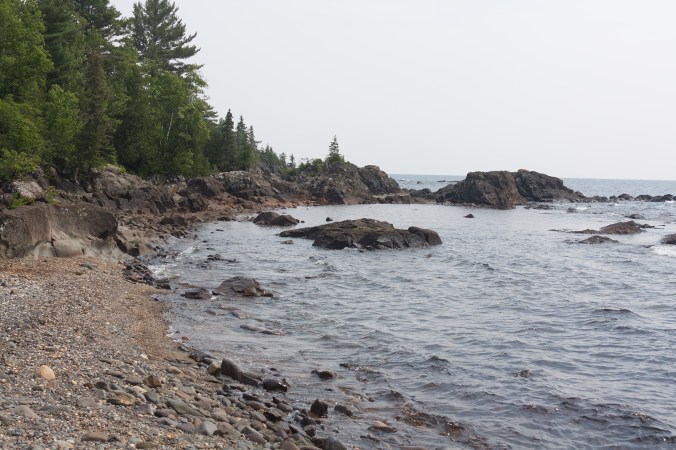
It was raining as I got out my camera to capture some of the eccentric houses on pilings, half-collapsed sheds, beached boats at low tide, old fishnet shacks with funky marine décor, scow houses, signs like “Don’t Mess with Nature”, and house boats floating with the tides. One stilted house featured an entrance way roof made by an inverted boat and a porch railing made of boat engines.
Finn Slough, BC (photo by Nina Munteanu)
.
.
This settlement was built by Finnish fishermen over a hundred years ago. I had visions of people rowing their boats around the slough—to the various wharfs, boardwalks, houses on pilings, and shores. Fishing for various Pacific Salmon (Chinook, Coho, Pink and Sockeye), Steelhead, Lingcod, Halibut, and Sturgeon. I’m told that this relic fishing village was one of several fishing shantytowns scattered along the shores of the Fraser River. Around 70 households existed in Finn Slough in the ‘40s to ‘50s; 30 people live there now. Most, I’m told, are an eclectic mixture of artists, musicians, and actors. Dorrington writes: “This historic settler village and important natural habitat is an intertidal Slough—a place of transitions, with the ebb and flow of tides, migrating birds, indigenous plants and animals. This Slough is an important safe haven for juvenile Salmon and other wildlife, as with all wetlands, it is an important ecosystem.”
.
.
Blogger Eve Lazarus contemplates the colourful history of this unique settlement that some call charming and others would describe as a chaotic decrepit mess of squatters in a drowning marsh: “the back-to-the-landers, the evil property developer from back east who wants to pave over the shanty town with condos and a park, and a few levels of government that would rather fill pot holes than be caught up in this drama. Ironically, it’s the red tape that seems to be the saviour in this story.”

I walked gingerly on the rickety wooden bridge that leads to several homes on Gilmour Island and stopped at the sign warning me that I was crossing at my own risk. I found myself thinking ‘who lives here? What kind of person chooses to stay here, in this uncertain environment where the direct effects of climate change relentlessly threaten?
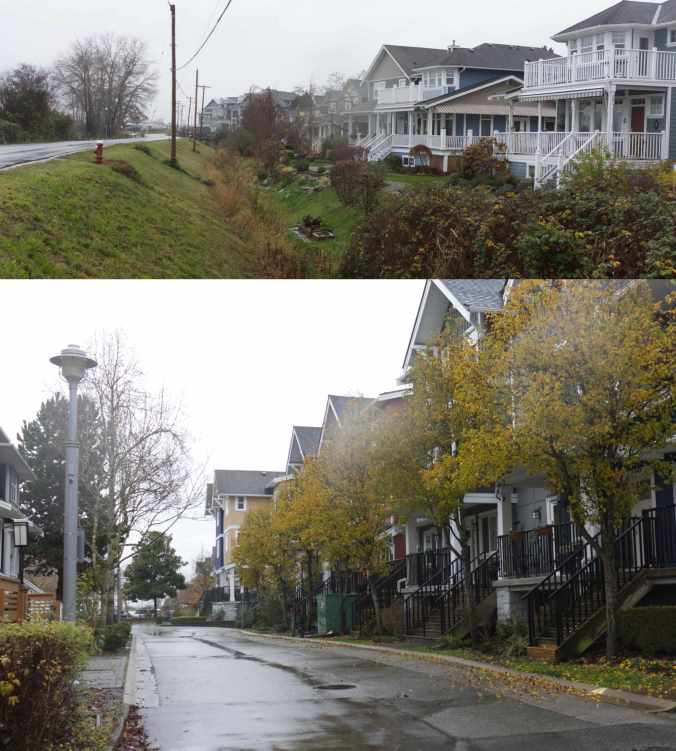
I thought of this as I drove west along Dyke Road toward No. 2 Road and encountered the contrast of posh Steveston Waterfront Estate houses with safe river views from behind dykes.
Sign on history of Finn Slough, BC (photo by Nina Munteanu)
.
.
Finn Slough & Climate Change
.
Gordon Katic of CBC tells us that Finn Slough lies on the front lines of climate change. “Nestled on the banks of the Fraser River, this community will eventually be overcome by flooding as sea levels rise.” I’m not surprised; the slough community lies on the edge of a saltwater marsh, ninahere describe more about marsh system. Coastal erosion from increased tanker traffic in the Fraser River has also increased, impacting the marsh’s ability to act as a buffer for wave action.
As climate-change increases the frequency and severity of flooding and coastal storm surges, BC municipalities are preparing for the sea level to rise by half a meter by the year 2050. Actions include investment in protective dikes. But Finn Slough’s homesteader community sits outside the dike system. Several homes have already flooded from seasonal high tides. Even the boardwalks that connected the homes flooded, leaving people stranded. Tamsin Lyle, engineer with Ebbwater Consulting says bleakly, “It’s not a good news story. Probably 60-70 years from now, this entire piece of land is going to be underwater every single day.”
Meantime, the community is finding ways to cope with the rise. One is simply to raise the houses currently on stilts. Gus Jacobson, community elder of Finn Slough, told the CBC that over his lifetime living there, the water has risen at least 18 inches. Jacobson is helping others in the community to raise their houses, docks, boardwalks and bridge. According to Jacobson, Finn Slough’s motto is “sisu”, a Finnish word that roughly translates to “stubborn perseverance.” The sign in front of the bridge defines “sisu” as Finnish for: endurance, resilience, tenacity, determination, perseverance and strength of will.
.
.
Stephen Sheppard, professor of landscape planning at the University of British Columbia, noted that the best option is a managed retreat: “Managed retreat refers to a strategy where over time the community or infrastructure that is at risk to sea level rise would get pulled back—literally removed—or in essence, relocated, or they might relocate themselves.”
Finn Slough is one of the last tidal communities on the West Coast and the last working commercial fishing village on the Fraser River. For over a hundred years this community has existed without official status or land tenure.
Charmed or doomed by climate change? Will the community adapt and prevail or exodus in the frustration and defeat of a ‘managed retreat’? Lyle gave CBC her prognosis: “I suspect that Finn Slough is going to be our canary in the region [Lulu Island].”
.
.
References:
Dorrington, David. “Finn Slough: where nature and history gently coexist,” sign located at Dyke Rd. at end of No. 4 Rd.
Katic, Gordon. 2017. “As a BC fishing village is slowly submerged, meet the people who refuse to leave.” CBC Radio, October 2. 2017
Lazarus, Eva. 2013. “Steveston’s Finn Slough.” Eve Lazarus Blog, September, 2013.
.
.

Nina Munteanu is an award-winning novelist and short story writer of eco-fiction, science fiction and fantasy. She also has three writing guides out: The Fiction Writer; The Journal Writer; and The Ecology of Writing and teaches fiction writing and technical writing at university and online. Check the Publications page on this site for a summary of what she has out there. Nina teaches writing at the University of Toronto and has been coaching fiction and non-fiction authors for over 20 years. You can find Nina’s short podcasts on writing on YouTube. Check out this site for more author advice from how to write a synopsis to finding your muse and the art and science of writing.
.