“There are women with voices and brains and power and intelligence that have been waiting for this moment.”—Director Jennifer Phang
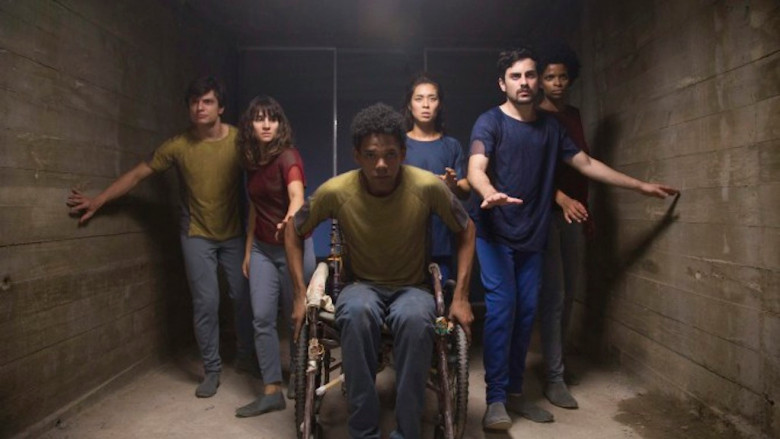
Advantageous is a low budget indie film by Jennifer Phang that explores a near-future world—a kind of “pre-dystopia”, according to Katharine Trendacosta of io9—where jobs have become heavily automated and opportunities for education are cutthroat. Women have been generally forced out of the workplace and onto the streets: the logic being that they will be less violent while living on the street than men.
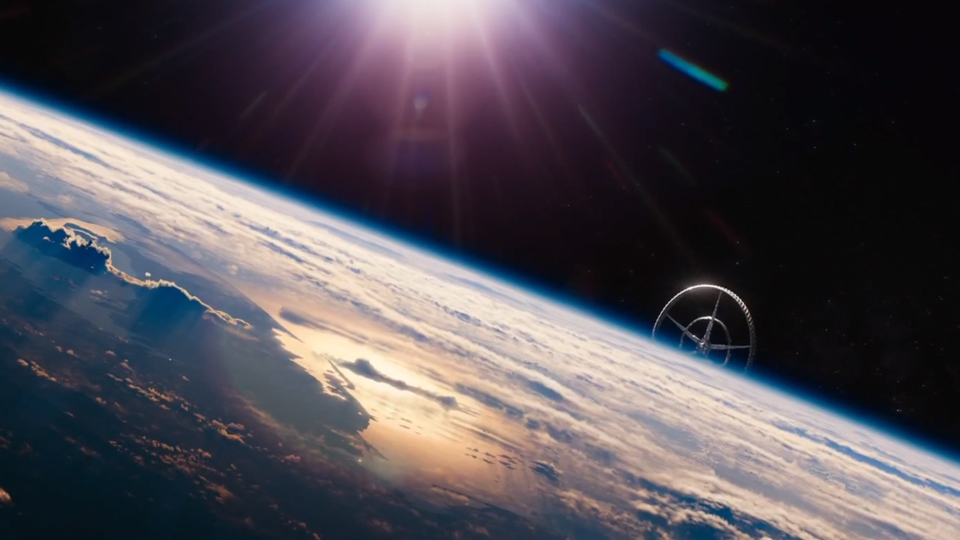
While the world vaguely resembles a vibrant City with flying ships and some bizarrely futuristic architecture (including a high rise that functions as a giant water feature), a sense of unease permeates most scenes, punctuated by occasional terrorist explosions and snippets of disturbing news reports. Artificial intelligence has supplanted most people in middle management, “The people you do see are either impoverished and disenfranchised or are hidden in the upper floors, the protected places,” says director Jennifer Phang. Unemployment is close to 50% and there are no public schools. The only options for a young girl—if she is not to end up on the streets, either as a beggar or prostitute—is to attend a highly selective free magnet school or a very expensive private school.

Gwen Koh (Jacgueline Kim) is the spokeswoman of the Center for Advanced Health and Living, a wellness corporation that offers health and beauty treatments to an elite who can afford it. When the Center informs her that she looks too old, Gwen—desperate to secure her bright daughter’s expensive education—submits to the experimental treatment she was initially hired to promote. Jules hadn’t made it into the free magnet school, leaving Gwen to come up with extensive funds to get her into a private school. The corporation has subtly backed Gwen into a corner by reminding her that her generation doesn’t have the skills to compete—all of education currently being STEM-based—and they fully understand that she is too old and too unconnected to do anything other than offer herself up to their new procedure to secure her position and a future for her daughter Jules. Constantly walking the edge of privilege, Gwen struggles to make the elite-connections necessary to place Jules. “Gwen is too old, too female, and too unconnected to do anything other than offer herself up as a sacrifice,” writes Trendacosta.
The true nature of her sacrifice is not understood at first; it unravels slowly, like an internal wound, until we learn that the procedure—putting her memories into a younger person’s body—means that Gwen’s “mother-connection” awareness with her daughter will be lost when her original body dies in the procedure. This is particularly significant, given their close and loving relationship, which is evocatively conveyed throughout the film.
Advantageous “is riveting, emotionally gripping, and offers up a vision of the future that is disturbingly easy to picture, even as some of the technologies it imagines seem out of reach,” says Ariel Schwartz of Business Insider Magazine. While the trope of mind-upload into a younger, prettier body has been around for while in standard SF, how Phang presents it, in the muted notes and pace of “everyday” and “mundane” events, brings a kind of realism to it that both invigorates and chills. Like watching a building explode in person rather than on TV. The immediacy and reality of it is visceral. Phang does this through sparing use of sound, language and colour. And all presented in a pace that does not rush, but lingers and reflects. Long moments of quiet punctuate scenes of significance, giving us the chance to examine, resonate and reflect in “real-time” with the character. These, in themselves, provide some of the most poignant footage of the film as we are given the time to descend into deeper reflection. Each plays out, short vignettes of life that string together like pearls on a necklace. Life moments. Unflinchingly and confidently performed at the pace of life.
In one of many quietly powerful scenes, Gwen stumbles upon a street woman, huddled in a small grassy alcove under an old blanket. When Gwen asks her if she is okay, the woman instead responds, “Are you okay?” This is a natural response for a woman; we think of others, of their welfare. We carry the “mother” archetype within us, everywhere we go, no matter what befalls us. This natural sense of compassion and altruism runs through our blood.
And, yes, it makes us a different kind of hero.
Gwen’s heroics are not accompanied by percussive violence or gut-wrenching action; they are silent choices that percolate from deep within. They are choices that ultimately bleed into great consequence.
“The plot suggests a standard ‘body swap’ sci-fi storyline,” says Danielle Riendeau of Polygon. “But Advantageous is much more about motherhood, the sacrifices women make for their children, and to a large extent, the difficulties of being a non-white woman in an increasingly intolerant society. The writing, directing and performances are so strong that they elevate the film far beyond a simple twist on a classic trope. Advantageous is a potent, heartbreaking meditation on parental love and the sacrifices women make for their families. It has a lot to say, and it does so with clear-eyed, fearless intensity.”
Trendacosta writes, “People are going to judge Advantageous by the things it lacks. There are no battles, no mustache-twirling villains, and not even any giant science fiction spectacle sets. People are also going to judge it for what it has. There are some intense discussions of classism, racism, ageism, sexism, and elitism. But don’t judge this movie for either of those things—instead, it’s worth appreciating for all the things it does so incredibly well.”
What Advantageous does so incredibly well is portray a near-future vision worth pondering and discussing.

Nina Munteanu is a Canadian ecologist / limnologist and novelist. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” was published by Mincione Edizioni in Rome. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press (Vancouver) was selected by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times ‘Year in Reading’ and was chosen as the 2017 Summer Read by Water Canada. Her novel “A Diary in the Age of Water” was released by Inanna Publications (Toronto) in June 2020.