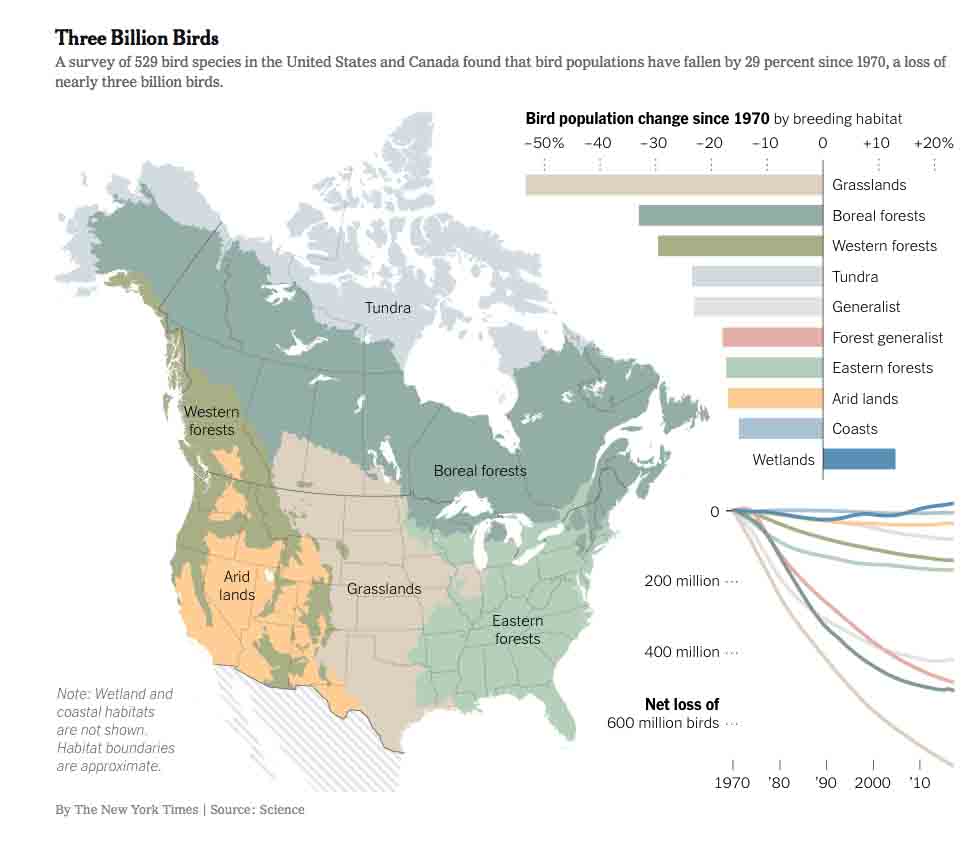
Not long ago, I was driving through a short tunnel that I typically take to go to work and, glancing back through the rearview mirror, I didn’t see what I expected to see. For some reason—perhaps it was the light or my wandering mind—the familiar scene looked unfamiliar; it was as though I’d entered a new dimension.
It felt ‘Otherly’ and I briefly experienced a titillating excitement akin to a protagonist journeying into a new world in some novel.
Indeed, the rhetoric of ‘Otherness’ in most fiction is typically portrayed through the singular point of view (POV) and discourse of a protagonist on a journey. The very nature of the term ‘Other’ used in any narrative suggests exclusion. According to Patricia Kerslake of Central Queensland University, the postcolonial notion of the Other arises through a mutual process of exclusion that inspires the very idea of ‘alien’ by imposing expectation on perception. Kerslake argues that: “When one culture imposes its perceptions on another, in that it begins to see the Other not as they are but as, in [Edward W.] Said’s words, ‘they ought to be’, then the process of representation becomes inevitable: a choice is made to see a ‘preferred’ real”.
In most forms of literature The POV ‘voice’ represents the Self, the inclusive ‘us’ (worldview) in its encounter with the Other, which in turn is the ‘not us.’ In his book Orientalism: Western Conceptions of the Orient Edward W. Said contended that for there to even be an ‘us’, there has to be a ‘not-us’. The resulting power dynamic of “them and us,” of Other and Self, is created and controlled by perceptions of the singular POV voice that usually represents ‘us.
‘The Other’ in Various Genres of Literature
In most genres of literature, the Other is often relegated to this dichotomous portrayal. In post-apocalyptic and metaphoric journey stories the Other may be the harsh environment or a calamity through which the protagonist must find their own strength to survive; in military stories it is clearly the enemy, seldom portrayed with compassion or understanding but there to test our hero; in coming-of-age stories it may be the oppressive rule or established world the hero must overcome; in science fiction it may be the hostile or unknowable aliens who must be defeated. According to Ursula K. Le Guin, science fiction displays a legacy of silencing the Other and rendering it impotent to establish and confirm humanity’s superior position in the world. Given that science fiction (SF) literature is rooted in culture, and often helps construct national identity, SF often confirms worldview, and in so doing creates internal Others (Brioni and Comberiati). According to Hermann, by failing to escape our boundary conflicts, SF simply constructs “new situations of restriction and otherness.” Kerslake argues that “silencing the Other provides SF with an indirect ability to define the potential of humankind”.1
‘The Other’ in Eco-Literature
While eco-literature overlaps with many genres, it appears to differ from SF and other genres portrayal of Other through its unique intention to give voice to otherwise voiceless characters, and it often does this through masterful use of character-coupling. Mary Woodbury defines eco-literature or eco-fiction as literature “made up of fictional tales that reflect important connections, dependencies, and interactions between people and their natural environments.” The environment—or an aspect of the environment—plays a major role in eco-literature, either as premise or as itself a character on a journey.
Eco-Literature is preeminently the literature of bringing awareness to the plight of the environment as both character and as Other and explores humanity’s role in that plight.
Eco-literature may go beyond raising awareness to link environmental abuse with concepts of jingoistic hubris; it may raise issues of human intersectionality, misogyny, marginalization, oppression of class, privilege, sexuality and race, and misuse of power. Violent acts perpetrated on environment—when environment is personified as ‘character’ and/or coupled directly to a character—elicit powerful emotion and clearly demonstrate how social/human injustice reflects environmental injustice.
At the heart of much eco-literature lie strong relationships forged between a major character (often main protagonist) and a minor character (as avatar for the environment such as place or ecosystem, a being, animal or plant) or an aspect of their environment—itself a character and archetype. The strong connection between protagonist and environment—whether antagonistic or sympathetic—fosters unique communication that provides ‘voice’ to the environment as Other and as Othered. The environment may serve as a symbolic connection to theme and can illuminate through the sub-text of metaphor a core aspect of a main or minor character and their journey: the over-exploited white pine forests for the lost Mi’kmaq in Annie Proulx’s Barkskins; the mystical life-giving sandworms for the beleaguered Fremen of Arrakis in Frank Herbert’s Dune.

Giving Voice to the Other Through Character-Coupling
The coupling of protagonist with avatar—character-coupling—creates powerful drama and visceral connection to environmental issues and needs. Character-coupling characterizes environment, the Other, and effectively provides it with a voice, often through relationship. It elicits reader engagement, sparking new understandings and motivations toward a better caring of this world. The Other’s voice may be understandable (e.g. in many fables such as The Bear), arcane, tumultuous or fearsome (Memory of Water), or enduring and silently profound (The Breathing Hole).
Eco-literature is particularly poised to make meaningful character-couplings between mostly human protagonist and environmental characters or representatives. This is because the protagonist provides relatable qualities for easy reader empathy, while the Othered character is often less relatable—often an arcane aspect of the environment, such as water (Memory of Water) or a forest (The Overstory). Character-couplings illuminate a core aspect of the main character’s journey and/or the reader’s journey. From direct and intimate (The Breathing Hole, The Bear) to associated and inferred (The Windup Girl, Barkskins), different forms of character couplings often provide a new understanding of the plight and viewpoint of the Other. The protagonist’s link to the Other provides a readable map for the reader to follow and make their own connection.2
Women Coupled with Nature as Other
Since before the industrial revolution, and very much to this day, the prevailing western worldview toward the wildness of nature has been to dominate it and constrain it. The conviction that humans are separate from and superior to nature was established by Judeo-Christian beliefs and the Cartesian hegemony that laid the foundations of modern anthropocentrism (White). Ecofeminist Ynestra King argues that “we live in a culture that is founded on the repudiation, [exploitation], and domination of nature … the Other that has no voice”. King further argues that, “Women, who are identified with nature, have been similarly objectified and subordinated in patriarchal society”.
The modern ecofeminist movement contends that a long historical precedent of associating women with nature has led to the oppression of both. Ecofeminists note that “women and nature were often depicted as chaotic, irrational, and in need of control, while men were frequently characterized as rational, ordered, and thus capable of directing the use and development of women and nature” (Miles).
French philosopher and writer Simone de Beauvoir elegantly explores this connection:
Man seeks in woman the Other as Nature and as his fellow being. But we know what ambivalent feelings Nature inspires in man. He exploits her, but she crushes him, he is born of her and dies in her; she is the source of his being and the realm that he subjugates to his will; Nature is a vein of gross material in which the soul is imprisoned, and she is the supreme reality…Woman sums up Nature as Mother. Wife, and Idea; these forms now mingle and now conflict, and each of them wears a double visage.
Simone de Beauvoir
Because of this association and history, some of the most powerful character-couplings in eco-literature are of women protagonists coupled with natural avatar: the Inuk widow with polar bear cub in the clifi allegory The Breathing Hole; the girl and bear in the allegory-fable The Bear; the windup girl Emiko and the Cheshire cats in the cautionary tale The Windup Girl; the tea master Noria and water in the post-ecosystem collapse novel Memory of Water; the ecologist, Patricia Westerford, with the giant trees in The Overstory.3
Part 2 (“Types of Character-Coupling in Seven Examples of eco-Literature“) follows next week.
Footnotes:
- The Other has often been metaphorically portrayed in SF by aliens that lack a distinct voice or viewpoint; some portrayal has reflected a fearful imperialistic colonialism by representing Other as adversary such as an invading monster with no regard for humans (e.g. Robert Heinlein’s The Number of the Beast; H.G. Wells’s War of the Worlds). Kerslake argues that the traits of the Other “fall characteristically—and conveniently—into those spaces we choose not to recognize in ourselves, the ‘half-imagined, half-known: monsters, devils, heroes, terrors, pleasures, desires’ of Said’s ‘Orient’”. The Martians of Ray Bradbury’s Martian Chronicles—who also have no voice—reflect our indigenous peoples under the yoke of settler colonialism and an exploitive resource-extraction mindset. The monster of Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein—also with no voice—exemplifies the disabled/deformed unsavory departure from our ‘perfect’ self-image; to be chased, destroyed and nullified.
- In some stories the protagonist is Othered in some way, providing a more direct link to the experience of being the Other or being Othered. For instance, in Mishell Baker’s Borderline, disabled protagonist Millie provides the connection to the greater theme of Othering “lesser beings.” In Costi Gurgu’s Recipearium, the protagonists are not human; they are alien creatures that dwell inside the dead carcass of a monster, representing Other as main character.
- Excellent examples that overtly deal with some of these injustices include The Fifth Season trilogy by N.K. Jemisin and The Marrow Thieves by Cherie Dimaline.
References:
Agamben, Giorgo. Homo Sacer: Sovereign Power and Bare Life. Stanford University Press. 1998. 228pp.
Bacigalupi, Paolo. The Windup Girl. Night Shade Books, New York. 2015. 466pp.
de Beauvoir, Simone. “The Second Sex.” Modern Library, Random House, New York. 1968. p.144 In:
Dwyer, Jim. Where the Wild Books are: A Field Guide to Ecofiction. University of Nevada Press, Reno, Nevada. 2010. 264pp.
Ganz, Marshall and Emily S. Lin. “Learning to Lead: a Pedagogy of Practice.” The Handbook for Teaching Leadership: Knowing, Doing, and Being, edited byIn Scott A. Sook, Nitin Nohria, and Rakesh Khurana. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications, 2012. 354p.
Herbert, Frank. Dune. Ace, New York. 1965. 884pp.
Itäranta, Emmi. Memory of Water. Harper Voyager. New York. 2014. 266pp.
Kerslake, Patricia. “The Self and Representations of the Other in Science Fiction.” Chapter 1. Science Fiction and Empire, Liverpool University Press, 2007, pp. 8-24.
King, Ynestra. “The Ecology of Feminism and the Feminism of Ecology.” Chapter 2. Healing the Wounds: The Promise of Ecofeminism, edited by Judith Plant. New Society Pub, 1989, pp. 18-28.
Krivak, Andrew. The Bear. Bellevue Literary Press, New York, NY. 2020. 221pp.
Miles, Kathryn. “Ecofeminism: sociology and environmentalism.” Britannica, britannica.com/topic/ecofeminism.
Murphy, Coleen. The Breathing Hole. Playwrights Canada Press, Toronto. 2020. 305pp.
Nugent, Brittany. “The Rare Bear Protecting a Canadian Rainforest.” Goodness Exchange. 2021. https://goodness-exchange.com/spirit-bear-kermode-bear-kept-a-secret-for-generations/ Accessed October 30, 2022.
Powers, Richard. The Overstory. W.W. Norton & Company, New York. 2018. 502pp.
Proulx, Annie. Barkskins. Scribner, New York. 2016. 717pp.
Roburn, Shirley. Shifting Stories, Changing Places: Being Caribou and Narratives of Transformational Climate Change in Northwestern North America. Concordia University PhD dissertation. P. 31. https://spectrum.library.concordia.ca/id/eprint/980193/1/Roburn_PhD_F2015.pdf. Accessed 31 October 2022
Said, Edward W. Orientalism: Western Conceptions of the Orient. Vintage, London, 1978. 432pp.
Woodbury, Mary. “What is Eco-fiction?” Dragonfly.eco. 2016. https://dragonfly.eco/eco-fiction/ Accessed September 15, 2022.

Nina Munteanu is a Canadian ecologist / limnologist and novelist. She is co-editor of Europa SF and currently teaches writing courses at George Brown College and the University of Toronto. Visit www.ninamunteanu.ca for the latest on her books. Nina’s bilingual “La natura dell’acqua / The Way of Water” was published by Mincione Edizioni in Rome. Her non-fiction book “Water Is…” by Pixl Press (Vancouver) was selected by Margaret Atwood in the New York Times ‘Year in Reading’ and was chosen as the 2017 Summer Read by Water Canada. Her novel “A Diary in the Age of Water” was released by Inanna Publications (Toronto) in June 2020.